Cómo transcribir correctamente una entrevista: una guía completa...
Aprende a transcribir correctamente una entrevista con esta guía completa. Obtén consejos prácticos sobre herramientas, edición y formato para transcripciones precisas.
Kate, Praveen
July 2, 2025
Cuando la gente habla de transcribir una entrevista, se refiere a convertir las palabras habladas en un archivo de texto limpio y preciso. Pero es más que eso. Una buena transcripción captura el diálogo, anota las señales no verbales y tiene un formato que es fácil de leer y fiel a la grabación original.
Preparando el escenario para una transcripción perfecta

El secreto de un proceso de transcripción indoloro comienza mucho antes de pulsar grabar. Es una verdad simple que he aprendido por las malas: si entra audio basura, sale transcripción basura. Ninguna cantidad de edición puede arreglar realmente una grabación apagada y ruidosa.
Dominar la configuración transforma la transcripción de una tarea frustrante a una tarea rápida y sencilla.
¿Por qué la calidad del audio es importante?
El audio claro mejora drásticamente la precisión de la transcripción, ya sea que utilices servicios de IA o humanos. Incluso las mejores herramientas de transcripción tienen dificultades con el ruido de fondo, el habla superpuesta o las salas con eco. Invertir unos minutos en la configuración ahorra horas de edición más tarde.
No se trata de comprar un equipo caro de estudio; se trata de tomar algunas decisiones inteligentes por adelantado.
Un archivo de audio limpio es el factor más importante tanto para las herramientas de IA como para los transcriptores humanos. Cuando una grabación es cristalina, la IA puede alcanzar tasas de precisión muy superiores al 95%.
IA de última generación
Impulsado por Whisper de OpenAI para una precisión líder en la industria. Soporte para vocabularios personalizados, archivos de hasta 10 horas y resultados ultra rápidos.

Importar desde múltiples fuentes
Importa archivos de audio y video desde diversas fuentes, incluyendo carga directa, Google Drive, Dropbox, URLs, Zoom y más.

Detección de hablantes
Identifica automáticamente diferentes hablantes en tus grabaciones y etiquétalos con sus nombres.
Pero ese número se desploma en el momento en que el ruido de fondo o las voces superpuestas entran en escena.
Captura Audio Claro y Seguro desde el Principio
Tu objetivo número uno es capturar audio limpio para cada hablante. Esto significa simplemente reducir el ruido de fondo y asegurarte de que las voces sean fáciles de distinguir. No necesitas un estudio profesional para lograrlo.
Busca una habitación tranquila. Los muebles blandos como alfombras, cortinas o incluso algunas almohadas pueden hacer maravillas para reducir el eco. Evita las habitaciones con frigoríficos que zumban, aires acondicionados que pitan o ruido de tráfico de una ventana abierta. Si tu entrevista es remota, vale la pena pedirle a tu invitado que haga lo mismo.
Para conversaciones en persona, coloca un micrófono dedicado entre tú y tu invitado; un poco más cerca de ellos suele ser mejor. Incluso un smartphone colocado sobre un libro (para evitar vibraciones) puede servir en un apuro. Para llamadas remotas, unos auriculares básicos con micrófono son una mejora masiva en comparación con el micrófono integrado de un portátil. Para asegurarte de capturar todo perfectamente, es posible que desees explorar diferentes funciones de grabación de llamadas para encontrar lo que funciona para tu configuración.
Consejo Profesional: Siempre, siempre haz una rápida prueba de sonido. Graba 30 segundos de ti y tu invitado hablando, luego reprodúcelo. Escucha el volumen, la claridad y cualquier zumbido de fondo molesto. Este pequeño paso puede salvarte de una grabación completamente inutilizable.
Prepara a tu Entrevistado y a Ti Mismo
Una conversación fluida conduce naturalmente a una transcripción más limpia. Esto va más allá de tener buenas preguntas; quieres crear un entorno donde las personas no hablen constantemente unas sobre otras.
Aquí tienes una lista de verificación rápida para una excelente sesión de grabación:
- Obtén Consentimiento: Antes de grabar, simplemente pide permiso. Un simple "¿Te importa si grabo esto para mis notas?" es profesional y, en muchos lugares, un requisito legal.
- Fomenta las Pausas: Hazle saber a tu invitado que está totalmente bien tomarse un momento para pensar. Esto no solo produce respuestas más reflexivas, sino que también crea pausas naturales en el audio. Eso facilita mucho la identificación de quién está hablando más tarde.
- Practica la Escucha Activa: Esto es clave. Presta atención a lo que dice tu invitado en lugar de solo esperar tu turno para hablar. Harás mejores preguntas de seguimiento y evitarás interrumpir, una causa clásica de audio desordenado y superpuesto. Para una inmersión más profunda, consulta nuestra guía sobre qué es la escucha activa.
Eligiendo tu Kit de Transcripción: IA vs. Humano
Una vez que tu archivo de audio cristalino esté listo, te enfrentas a una gran decisión: ¿cómo convertirás esas palabras habladas en texto? Aquí es donde eliges tu herramienta principal, y las opciones realmente se reducen a tres caminos principales: depender de un humano, usar un servicio impulsado por IA o combinar ambos.
El camino que elijas impacta directamente en el costo, la velocidad y la precisión final de tu proyecto. No hay una única opción "mejor" aquí; la correcta depende completamente de lo que necesites para esta entrevista específica.
El Argumento a Favor de la Transcripción Humana
Cuando la precisión absoluta es innegociable, los transcriptores humanos siguen siendo el estándar de oro. Un profesional puede navegar conversaciones complejas con hablantes superpuestos, descifrar acentos densos e identificar correctamente jerga específica de la industria que podría desconcertar por completo a un algoritmo.
Por supuesto, esa precisión tiene sus inconvenientes. Es la opción más cara, generalmente se cobra por minuto de audio, y lleva más tiempo. Una entrevista de una hora puede llevar fácilmente a un profesional varias horas o incluso un día completo para transcribir perfectamente.
Un humano es esencial cuando las apuestas son altas: piensa en deposiciones legales, investigación académica publicada o una entrevista principal para una publicación importante donde cada palabra debe ser perfecta.
El Poder de la Transcripción con IA
En el otro extremo del espectro se encuentra la increíble eficiencia de la transcripción con IA. Las plataformas construidas sobre esta tecnología pueden procesar una hora de audio en solo unos minutos, entregando un borrador completo por una fracción mínima de lo que cobraría un servicio humano. Ese tipo de velocidad cambia las reglas del juego para proyectos con plazos ajustados o un alto volumen de contenido.
La transcripción por IA ha mejorado rápidamente
Los avances recientes en el reconocimiento de voz han reducido significativamente las tasas de error para grabaciones claras de un solo hablante. Las herramientas de IA modernas ahora admiten acentos, marcas de tiempo y etiquetado de hablantes con una precisión impresionante, lo que las hace viables para uso profesional.
Un ejemplo de ello es el servicio de transcripción de IA Parakeet, que muestra este enfoque moderno.
Sin embargo, la IA no es infalible. Sobresale con audio claro y de un solo hablante, pero su rendimiento puede disminuir con ruido de fondo, varios hablantes hablando unos sobre otros o terminología desconocida. Esto solo significa que siempre debes planificar pasar tiempo revisando y editando el borrador inicial generado por IA. Si deseas una inmersión más profunda en cómo funciona esta tecnología, consulta nuestra guía sobre cómo transformar audio a texto con IA.
Encontrar el punto óptimo con un enfoque híbrido
Para la mayoría de las personas, la solución más práctica es un modelo híbrido. Este método combina lo mejor de ambos mundos: comienzas con una transcripción de IA rápida y asequible y luego realizas una revisión humana final para detectar y corregir cualquier error.
Este enfoque te brinda la velocidad bruta de la automatización al tiempo que garantiza la precisión y los matices que solo un ojo humano puede proporcionar. Es el equilibrio perfecto para la mayoría de los casos de uso comunes, como crear contenido de blog a partir de un podcast, generar notas de reuniones o transcribir entrevistas para análisis interno.
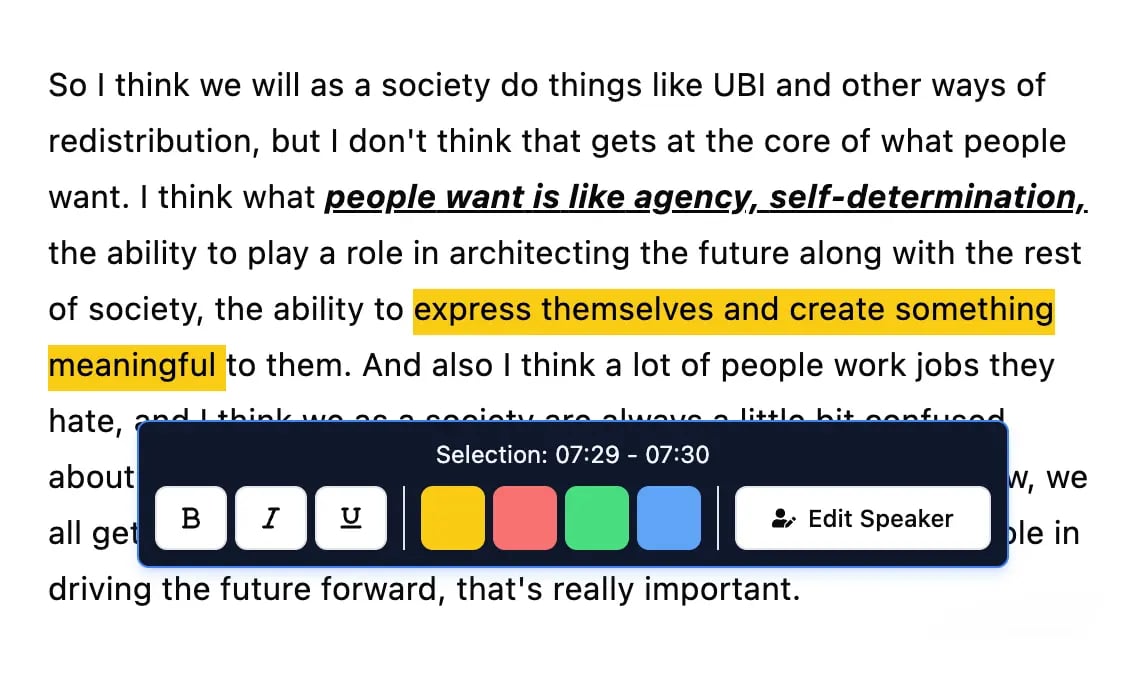
Herramientas de edición
Edita transcripciones con herramientas potentes como buscar y reemplazar, asignación de hablantes, formatos de texto enriquecido y resaltado.
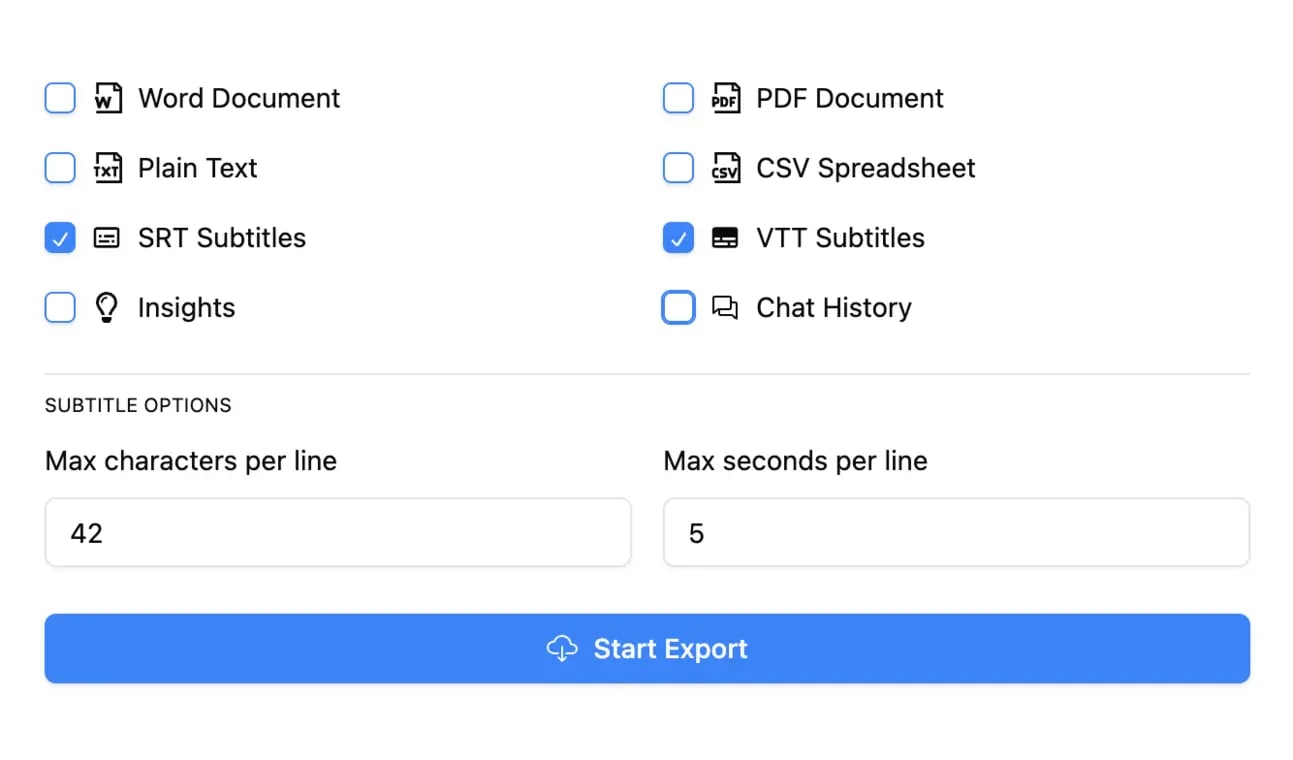
Exportar en múltiples formatos
Exporta tus transcripciones en múltiples formatos incluyendo TXT, DOCX, PDF, SRT y VTT con opciones de formato personalizables.
Resúmenes y Chatbot
Genera resúmenes y otros análisis de tu transcripción, prompts personalizados reutilizables y chatbot para tu contenido.
Veamos cómo se comparan estos tres métodos.
Comparación de Métodos de Transcripción: Costo, Velocidad y Precisión
| Método | Costo Promedio (por minuto de audio) | Tiempo de Entrega Típico (para 1 hora de audio) | Precisión (Tasa de Error de Palabra) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transcripción Humana | $1.50 - $5.00+ | 24 - 48 horas | < 2% |
| Transcripción con IA | $0.10 - $0.50 | 5 - 15 minutos | 8% - 18% |
| Híbrido (IA + Edición Humana) | $0.50 - $1.25 | 1 - 4 horas | < 5% |
Los datos realmente respaldan esto. Las evaluaciones de referencia muestran que, si bien los mejores motores de IA tienen tasas de error de palabras del 8% al 18% en condiciones ideales, estas pueden aumentar por encima del 25% en entrevistas ruidosas con varios hablantes. En contraste, los transcriptores humanos profesionales mantienen tasas de error por debajo del 2% en esas mismas condiciones difíciles.
El modelo híbrido cierra eficazmente esa brecha, a menudo reduciendo la tasa de error final a menos del 5% con solo un aumento modesto en su tiempo y esfuerzo.
Edición y Pulido de Tu Primer Borrador
Obtener esa transcripción en bruto, ya sea que te haya llevado horas de escritura manual o solo unos minutos con una herramienta de IA, es solo el primer paso. El verdadero arte de aprender a transcribir una entrevista correctamente ocurre en la edición. Aquí es donde transformas un revoltijo de palabras en un documento pulido, preciso y genuinamente útil.
Piensa en ese primer borrador como arcilla cruda. Tiene la forma básica, pero necesita una mano experta para alisar las imperfecciones y darle vida. Tu trabajo ahora es volver a escuchar el audio, comparándolo palabra por palabra con el texto.
Pasos clave para pulir una transcripción
Verificar la precisión del hablante
Etiquetar correctamente a los hablantes garantiza la claridad y evita la atribución errónea. La identificación clara es especialmente importante para entrevistas, investigaciones y documentación legal.
Resolver audio poco claro
Marcar las secciones inaudibles con marcas de tiempo en lugar de adivinar. Esto preserva la precisión y permite a los revisores futuros volver al audio original si es necesario.
Eliminar distracciones
Elimina palabras de relleno, inicios en falso y repeticiones innecesarias al crear transcripciones literales inteligentes. Esto mejora la legibilidad sin cambiar el significado.
Añadir señales contextuales
Las señales no verbales como la risa o las pausas añaden contexto emocional y conversacional. Cuando se usan con moderación, hacen que las transcripciones sean más informativas y humanas.
Estás buscando errores, aclarando partes confusas y asegurándote de que la transcripción final sea un reflejo fiel de la conversación.
Este diagrama de flujo desglosa el proceso básico de toma de decisiones cuando estás empezando, ayudándote a sopesar la necesidad de velocidad frente a la demanda de precisión.
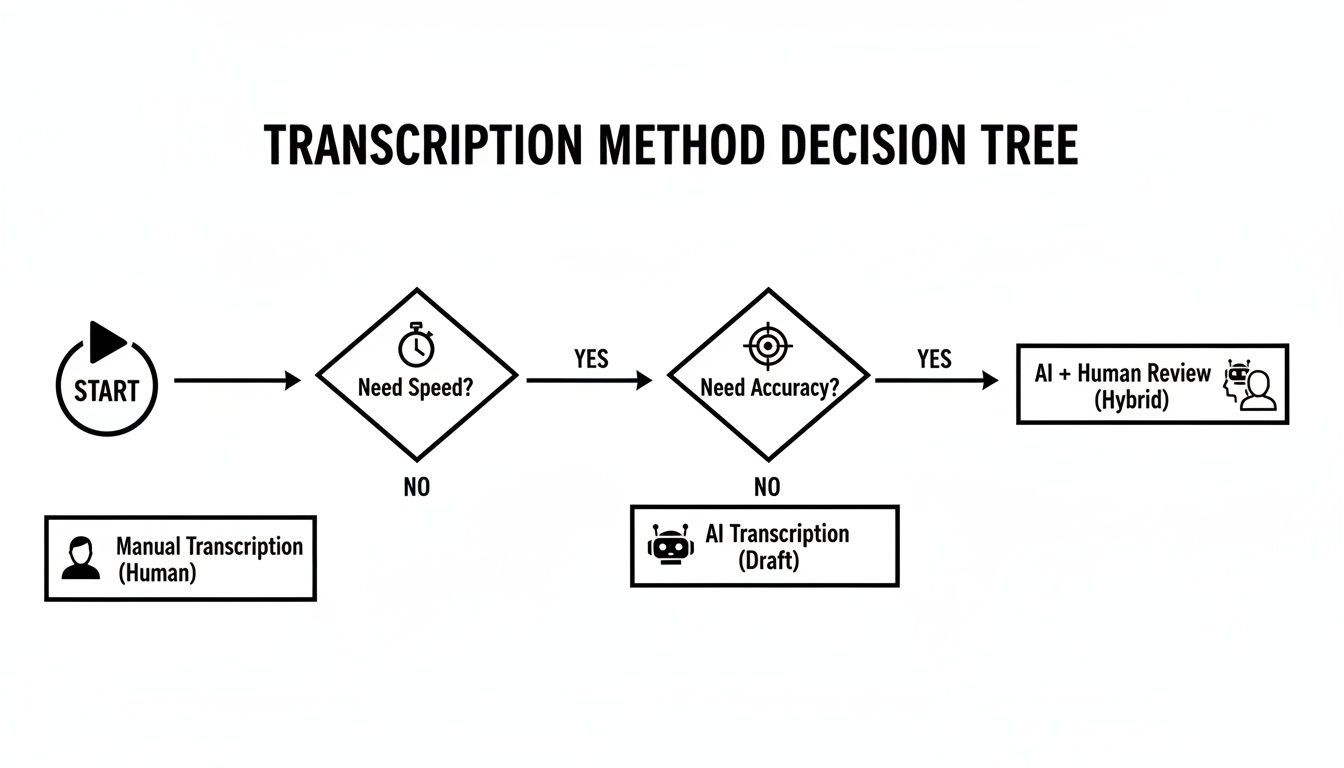
Como puedes ver, sin importar el camino que tomes inicialmente, una revisión humana final es casi siempre el último paso para garantizar una transcripción pulida y de alta calidad.
Decidiendo entre estilos de transcripción literal
Tu primera gran decisión es qué tipo de transcripción necesitas realmente. Esta elección dicta cómo manejarás toda la naturalidad del habla humana, y es una decisión crucial que debes tomar por adelantado.
- Literal estricto: Este es el enfoque de "tal cual". Capturas todo, cada "eh", "ah", tartamudeo y comienzo en falso. Es esencial para deposiciones legales o análisis cualitativos profundos donde cómo se dijo algo es tan importante como qué se dijo.
- Literal inteligente: Esto es lo que la mayoría de la gente busca. También conocido como "lectura limpia", eliminas todas las palabras de relleno, corriges pequeños tropiezos gramaticales y arreglas las oraciones largas para que el texto fluya. El objetivo es la máxima legibilidad sin cambiar el significado original del hablante. Es perfecto para crear artículos, publicar entrevistas o generar notas de reuniones.
Hacer esto bien desde el principio te ahorra un gran dolor de cabeza más adelante. No hay nada peor que tener que hacer una segunda edición, mucho más profunda, porque elegiste el estilo incorrecto.
Una transcripción de alta calidad no es solo un "extra agradable", tiene un impacto real. Un estudio encontró que los investigadores cualitativos que usaban transcripciones literales capturaron un 28% más de datos utilizables y redujeron la necesidad de volver a contactar a los entrevistados para aclaraciones en un 42%.
Tu flujo de trabajo de corrección
Bien, has elegido tu estilo. Es hora de sumergirse. No te limites a hojear el texto; necesitas escuchar activamente el audio mientras lees. Una herramienta con controles de reproducción integrados que puedas gestionar con atajos de teclado es un gran cambio aquí. Poder reducir la velocidad o saltar instantáneamente 5 segundos hace que todo el proceso sea mucho más fluido.
Mientras trabajas, presta atención a estas cosas clave:
- Etiquetas de hablante: Asegúrate de que cada hablante esté identificado correcta y consistentemente de principio a fin. "Hablante 1" y "Hablante 2" están bien, pero "Entrevistador" y "Dr. Smith" son mucho más claros para el lector final.
- Palabras inaudibles o poco claras: Cuando encuentres una parte del audio que simplemente no puedes entender, nunca adivines. Usa un marcador de posición con marca de tiempo como
[inaudible 00:15:32]o[unclear 00:21:10]. Esas marcas de tiempo son tu mejor amiga, permitiéndote a ti o a un colega saltar directamente al punto complicado más tarde. - Indicadores no verbales: Dependiendo de para qué sea la transcripción, es posible que desees anotar sonidos no verbales importantes. Etiquetas simples como
[laughter]o[crosstalk]pueden añadir una sorprendente cantidad de contexto que de otro modo se perdería en el texto.
Esta etapa de corrección es, sin duda, el paso más importante para garantizar que tu transcripción final sea precisa y fiable. Para dominar realmente este proceso, consulta nuestro análisis en profundidad de las mejores prácticas para corrección en transcripción. Un poco de tiempo dedicado a aprender lo básico aquí se amortiza enormemente en la calidad de tu trabajo.
Formateo de tu transcripción para uso profesional
Una transcripción precisa no sirve de nada si nadie puede leerla. Después de todo el arduo trabajo de edición y corrección, el paso final es formatear tu texto en un documento limpio, profesional y fácil de navegar. Esto es lo que convierte un borrador en bruto en un activo final listo para revisión legal, investigación académica o creación de contenido.
El objetivo es bastante simple: hacer que el documento sea lo más fácil de usar posible. El formato adecuado no se trata solo de que las cosas se vean bien; se trata de funcionalidad. Permite a un lector escanear rápidamente la información clave, identificar quién está hablando y encontrar momentos específicos en la grabación sin tener que hurgar en un muro de texto.
Construyendo un diseño coherente y legible
La coherencia lo es todo en una transcripción profesional. Cada entrevista que transcribas debe seguir el mismo conjunto de reglas, lo que hace que tu trabajo sea fiable y comprensible al instante para cualquiera que lo utilice.
Primero, establece etiquetas de hablante claras. Usar el nombre real de la persona o un título descriptivo (como Entrevistador o Dr. Evans) es mucho mejor que etiquetas genéricas como "Hablante 1". Siempre haz que estas etiquetas sean negritas y úsalas de la misma manera en todo el documento.
Por ejemplo:
Jessica Kent: El primer paso es siempre preparar a fondo la entrevista. Necesitas conocer tu tema a fondo.
Entrevistador: ¿Cómo cambia esa preparación tu línea de preguntas?
Este simple cambio le dice inmediatamente al lector quién está hablando, haciendo que la conversación sea pan comido de seguir. Otro gran cambio es el uso de marcas de tiempo. No necesitas tenerlas en cada línea, pero incluirlas a intervalos regulares, tal vez cada párrafo o cada 30-60 segundos, proporciona puntos de referencia invaluables.
Una marca de tiempo bien colocada, como
[00:15:32], actúa como un faro de navegación. Permite a un lector saltar instantáneamente a ese punto exacto en el audio para verificar una cita o captar el tono del hablante. Para cualquier tipo de trabajo periodístico o legal, esto es innegociable.
Manejo de indicadores no verbales y audio poco claro
Las conversaciones reales son desordenadas. Tu transcripción necesita un sistema estandarizado para manejar todas las partes que no son diálogos limpios. Estas pequeñas notas añaden un contexto crucial que de otro modo se perdería por completo.
Aquí están las anotaciones esenciales que querrás incluir:
- Habla inaudible: Cuando genuinamente no puedas entender una palabra o frase, usa una nota entre corchetes con una marca de tiempo. Algo como:
[inaudible 00:08:14]. Hagas lo que hagas, nunca adivines lo que se dijo. - Solapamiento: Si los hablantes comienzan a hablar uno sobre el otro y el diálogo se vuelve confuso, un simple
[crosstalk]es todo lo que necesitas para explicar la superposición. - Sonidos no verbales: Sonidos contextuales como
[laughter],[applause]o[phone ringing]deben incluirse para pintar una imagen más completa de lo que estaba sucediendo en la sala.
Finalmente, piensa en el formato del archivo. Si bien un archivo .txt simple es universal, exportar a .docx o .pdf es lo que fija todo tu cuidadoso formato. Un archivo .docx es ideal para colaboradores que puedan necesitar hacer sus propias ediciones, mientras que un .pdf es perfecto para crear una versión final e inalterable para su distribución. Al dominar estos detalles, aprendes cómo transcribir correctamente una entrevista de principio a fin.
Navegando la confidencialidad y la seguridad de los datos

Las palabras de tu entrevista son importantes, pero proteger la información detrás de ellas es igual de crítico. Cuando transcribes una entrevista, no solo estás escribiendo; estás manejando datos potencialmente sensibles, y eso conlleva serias responsabilidades éticas y legales.
Todo comienza con el consentimiento informado. Antes de que pienses en presionar el botón de grabar, tu entrevistado necesita saber exactamente lo que está sucediendo. Un rápido "¿Está bien si grabo esto?" ya no es suficiente. Necesitan entender cómo se utilizará la grabación y la transcripción, dónde se almacenarán y quién podrá verlas.
Anonimización y protección de identidades
Para una gran cantidad de proyectos —investigación académica, periodismo, sesiones de retroalimentación de usuarios— mantener la identidad de tu participante en secreto es innegociable. El método más común es la anonimización, que significa eliminar metódicamente cualquier información de identificación personal (PII) del texto.
Esto es más que solo eliminar su nombre. Debes estar atento a otros identificadores:
- Nombres de empresas o equipos específicos
- Cargos o ubicaciones precisas
- Nombres de colegas, familiares o amigos
- Cualquier otro detalle único que pueda señalar accidentalmente hacia ellos
Un truco común es reemplazar los nombres por códigos genéricos como "Participante A" o "Entrevistado 1". Si necesitas reidentificarlos más tarde para tus propios registros, puedes mantener una clave separada y almacenada de forma segura. Es un paso simple que contribuye enormemente a generar confianza.
Tu deber de cuidado cubre todo el ciclo de vida de los datos de la entrevista. Desde el momento en que capturas el audio hasta el día en que finalmente archivas o eliminas la transcripción, cada acción requiere una mentalidad de seguridad primero.
Prácticas seguras de almacenamiento y transferencia
Cómo gestionas los archivos reales es una gran parte del rompecabezas de seguridad. Enviar archivos de audio o transcripciones por correo electrónico como archivos adjuntos normales es un gran riesgo, ya que el correo electrónico estándar no está cifrado. Debes utilizar métodos seguros tanto para almacenar como para enviar tus datos.
Evitar el intercambio inseguro de archivos
Los correos electrónicos sin cifrar y los enlaces de archivos públicos exponen datos sensibles de la entrevista a graves riesgos. Utiliza siempre almacenamiento cifrado, controles de acceso y enlaces de uso compartido que caduquen, especialmente al manipular material legal, médico o confidencial.
Usar almacenamiento en la nube cifrado con controles de acceso estrictos es un excelente punto de partida. Cuando llegue el momento de compartir, utilice servicios que le permitan crear enlaces seguros y protegidos con contraseña que expiren. Esto reduce la ventana de vulnerabilidad y ayuda a garantizar que solo las personas adecuadas obtengan acceso.
Para cualquiera que trabaje con información médica, las reglas se vuelven aún más estrictas. Si ese es usted, consulte nuestro análisis detallado sobre servicios de transcripción que cumplen con HIPAA para asegurarse de que está bien preparado.
Algunas preguntas comunes sobre transcripción
Cuando estás empezando a averiguar cómo transcribir una entrevista, siempre surgen algunas preguntas. Todo el proceso puede parecer un poco abrumador, pero una vez que entiendes un par de ideas clave, tu flujo de trabajo será mucho más fluido.
Abordemos algunos de los obstáculos más frecuentes con los que se encuentran las personas. Uno de los más importantes es simplemente comprender el compromiso de tiempo: es increíblemente fácil subestimar cuánto tiempo realmente lleva.
¿Cuánto tiempo se tarda en transcribir una hora de audio?
Honestamente, el tiempo que lleva transcribir una hora de audio es muy variable. Realmente depende de tu experiencia y de lo limpio que sea el audio.
Un profesional experimentado que trabaja con una conversación clara entre dos personas probablemente pueda transcribir una hora de audio en unas 3 a 4 horas. Eso es bastante rápido.
Pero para un principiante, o para cualquiera que se enfrente a un audio desordenado (piensa en varios hablantes que se interrumpen, acentos marcados o mucho ruido de fondo), ese tiempo puede extenderse fácilmente a 6 a 8 horas, o incluso más. Esa gran diferencia es exactamente la razón por la que los servicios de transcripción por IA están despegando. Pueden generar un primer borrador en 10-15 minutos, dejándote con la tarea mucho más fácil de revisar.
¿Cuál es el mejor software para transcribir entrevistas?
No existe una única herramienta "mejor", porque todo depende de lo que intentes lograr. El software adecuado realmente depende del trabajo.
- Para velocidad y valor: Aquí es donde las plataformas impulsadas por IA como Transcript.LOL, Otter.ai o Descript realmente brillan. Te dan un borrador sorprendentemente bueno en minutos, lo que te salva la vida en plazos ajustados.
- Para máxima precisión: Si cada palabra tiene que ser perfecta, especialmente con audio difícil, un servicio humano como Rev o GoTranscript a menudo vale la pena la inversión.
- Para edición manual: Muchos profesionales, incluyéndome a mí, utilizan un enfoque híbrido. Comenzamos con un borrador de IA y luego usamos una herramienta dedicada como Express Scribe para limpiarlo. Sincroniza la reproducción de audio con tu editor de texto, haciendo que las correcciones sean mucho más eficientes.
El flujo de trabajo más efectivo hoy en día a menudo combina la velocidad bruta de la IA con el pulido final de un editor humano. Obtienes una gran ventaja inicial de la IA, luego puedes concentrarte en perfeccionar los detalles sin el alto costo de un servicio completamente manual.
¿Debo incluir palabras de relleno como "eh" y "ah"?
Todo esto se reduce al propósito de tu transcripción. Deberás decidir el estilo antes de comenzar a editar, ya que dicta cómo manejas estos pequeños detalles.
Si necesitas una transcripción literal estricta, entonces sí, tienes que incluir cada sonido. Eso significa que todos los "eh", "ah", tartamudeos y comienzos en falso se quedan. Este estilo es innegociable para cosas como procedimientos legales o investigación académica profunda donde cómo se dijo algo es tan importante como qué se dijo.
Para casi todo lo demás (convertir una entrevista en una publicación de blog, publicar un Q&A o simplemente obtener notas de reuniones limpias), una transcripción literal inteligente es el camino a seguir. Este estilo "limpio" elimina todas las palabras de relleno y corrige errores menores de gramática, haciendo que el texto fluya sin problemas y se lea fácilmente sin cambiar el mensaje real del hablante.
¿Listo para convertir tu audio en texto preciso y editable en minutos? Con Transcript.LOL, obtienes la velocidad de la IA de primer nivel combinada con potentes herramientas de edición, detección de hablantes y múltiples opciones de exportación. Deja de pasar horas escribiendo y empieza a crear. ¡Prueba Transcript.LOL gratis hoy mismo!
