hipaa compliant transcription services: Secure, trusted
A practical guide to hipaa compliant transcription services: protect patient data, meet security standards, and choose the right partner.
Kate, Praveen
August 14, 2024
When you're dealing with patient information, choosing a transcription service isn't just about speed or accuracy—it's about staying on the right side of the law. HIPAA compliant transcription services are built specifically to turn audio or video containing Protected Health Information (PHI) into text, all while meeting strict federal security rules.
This isn't just a "nice-to-have." It's a legal must-have for protecting patient trust and dodging massive fines.
Decoding HIPAA Compliant Transcription
Think of a standard transcription service like sending a postcard. Anyone who gets their hands on it can read what's written. HIPAA compliant transcription services, on the other hand, are like a sealed, armored truck. Every word is locked down from the moment it's recorded until it’s delivered, keeping sensitive patient data completely confidential.
That one difference is everything for any organization handling PHI.
Powerful Features That Make Secure Transcription Easier
State-of-the-art AI
Powered by OpenAI's Whisper for industry-leading accuracy. Support for custom vocabularies, up to 10 hours long files, and ultra fast results.

Import from multiple sources
Import audio and video files from various sources including direct upload, Google Drive, Dropbox, URLs, Zoom, and more.
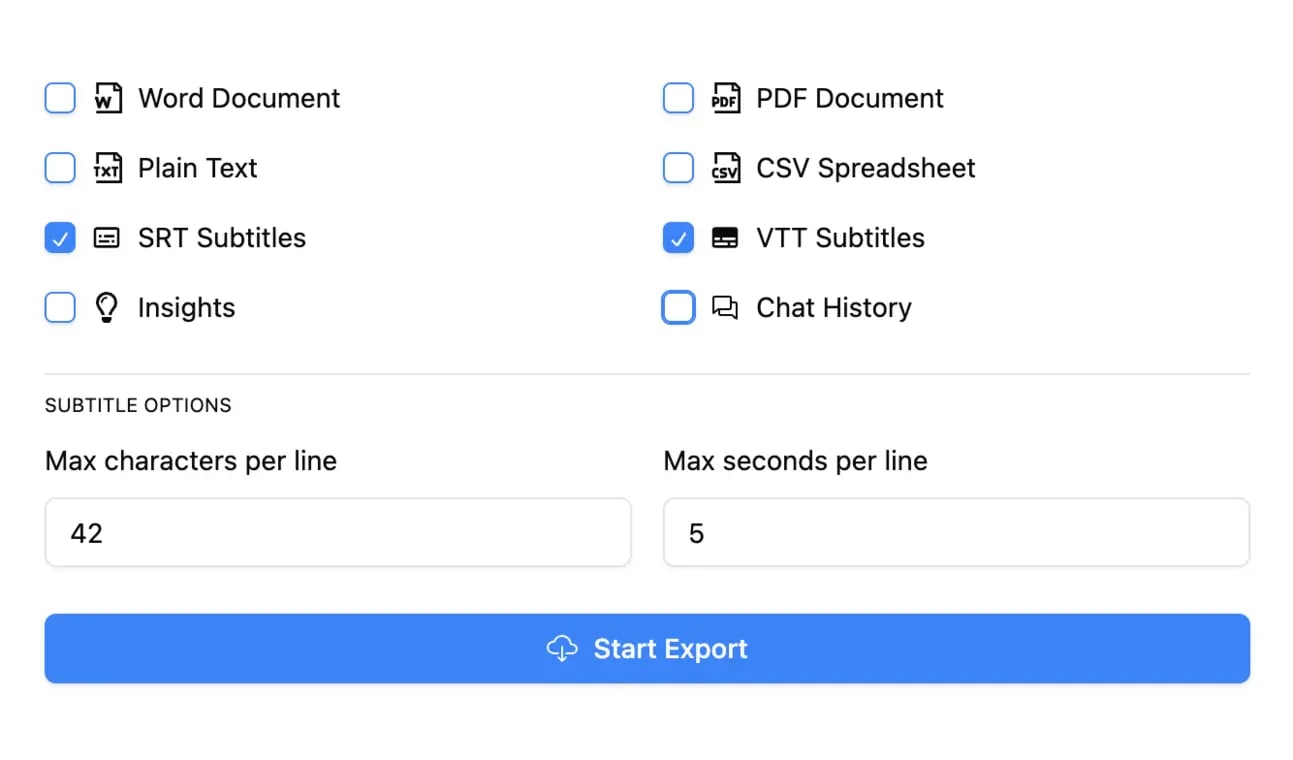
Export in multiple formats
Export your transcripts in multiple formats including TXT, DOCX, PDF, SRT, and VTT with customizable formatting options.
The Core Purpose and Growing Need
The whole point is to create accurate medical records—from dictated clinical notes and patient consults to telehealth calls—without breaking the strict privacy rules set by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). If a service "touches" PHI, even just to turn it into text, it absolutely must follow these security protocols.
And the demand for these services is exploding. The global medical transcription market hit US$ 82.1 billion in 2024 and is expected to rocket to US$ 145.9 billion by 2035. This surge is fueled by the move to electronic health records (EHRs) and regulators getting tougher, especially in North America. The full research report breaks down these trends even further.
Key Distinctions from Standard Services
So, what really separates a compliant service from a generic one? The gap isn't just in the features; it's a completely different legal and operational mindset.
To make this crystal clear, here’s a quick breakdown of what sets them apart.
Compliant vs Standard Transcription at a Glance
This quick comparison highlights the essential differences in security, legal obligations, and data handling between standard and HIPAA compliant transcription services.
| Feature | Standard Transcription Service | HIPAA Compliant Transcription Service |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Accountability | No legal liability for PHI breaches. | Signs a Business Associate Agreement (BAA), making them legally responsible for protecting PHI. |
| Data Security | Basic security, if any. Data may be unencrypted. | Implements mandatory administrative, physical, and technical safeguards, including end-to-end encryption. |
| Access Controls | Often lacks granular user permissions. | Enforces strict, role-based access controls to ensure only authorized personnel can view data. |
| Audit Trails | Typically no detailed logging. | Maintains meticulous audit trails logging every action taken on data for full accountability. |
| Data Handling | May process data offshore or on unsecured servers. | Follows strict protocols for data storage, transmission, and destruction to prevent unauthorized access. |
Ultimately, the choice comes down to one thing: risk. A standard service might get the words right, but a HIPAA compliant one provides legally defensible security.
A standard transcription tool might offer speed, but a HIPAA compliant service provides legally defensible security. Choosing the wrong one isn't a simple mistake; it's a compliance failure that can lead to severe penalties.
Getting these fundamentals right is the first step. For healthcare providers, using secure medical and healthcare transcription is non-negotiable for keeping things running smoothly while maintaining patient trust. This guide will show you exactly how to do it.
The Three Pillars of HIPAA Security in Transcription
HIPAA compliance isn't just a checkbox you tick off a list. Think of it more like building a secure fortress to guard sensitive patient data. You wouldn't just build a strong wall and call it a day, right? You'd also need guards, rules for who gets in, and a system to monitor everything.
This three-pronged approach is what makes a HIPAA compliant transcription service truly secure. It ensures Protected Health Information (PHI) is shielded from every possible angle. Understanding these pillars is the key to figuring out if you can really trust a vendor with your patients' data.
The infographic below shows the clear divide between standard transcription and services built from the ground up for HIPAA.
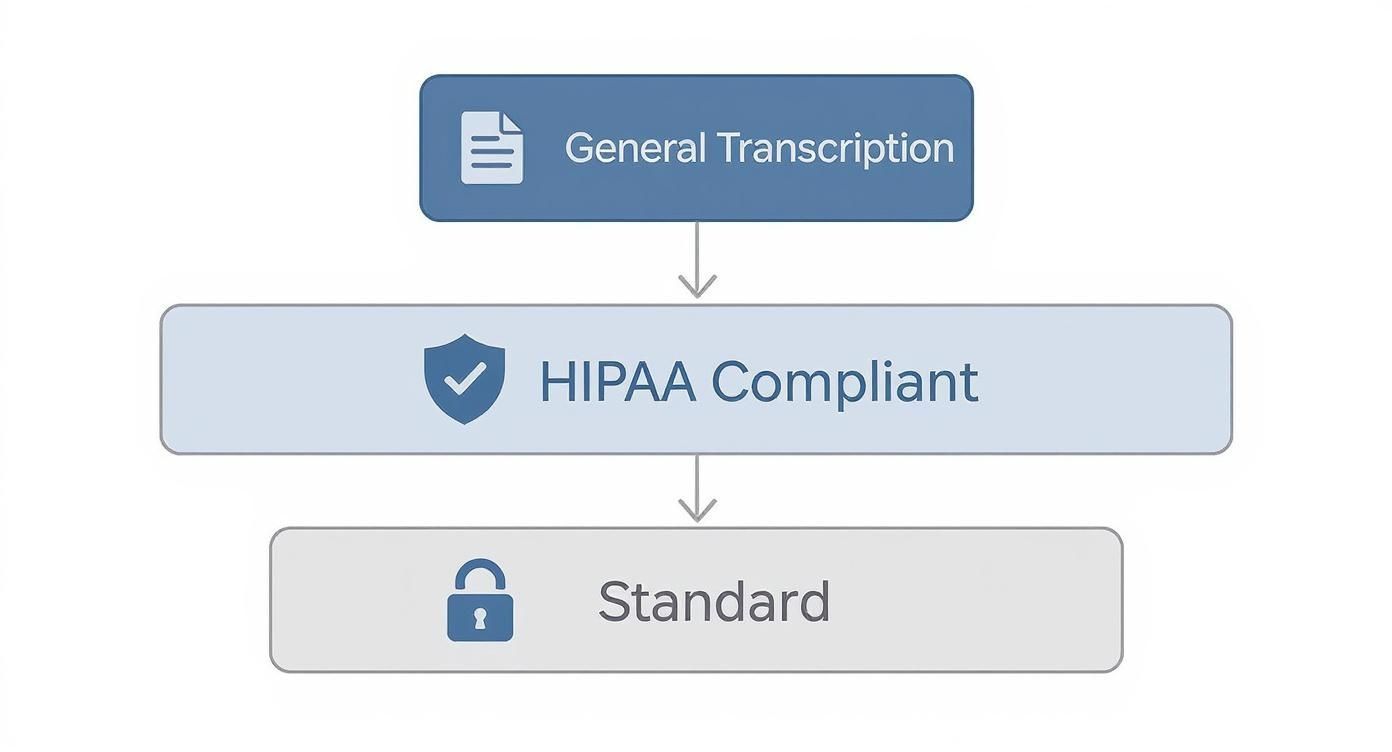
As you can see, HIPAA compliance is a specialty. Security isn't just an add-on; it's the entire foundation.
Why Standard Tools Fail HIPAA Immediately?
Most transcription services cannot meet HIPAA’s strict requirements, even if they claim security. Missing safeguards such as encryption, access control, or audit logs can put PHI at risk instantly. Using non-compliant tools can lead to major legal violations and patient data exposure.
Administrative Safeguards: The Rulebook
First up are the Administrative Safeguards. These are all the policies and procedures that dictate how an organization handles security. This is the "who, what, when, where, and why" of data protection—less about tech and more about documented human processes.
These safeguards define who can access PHI and under what specific conditions. Key components include:
- Security Management Process: This starts with a deep-dive risk analysis to spot potential weak points and then putting measures in place to patch them up.
- Assigned Security Responsibility: One person, typically a Security Officer, needs to be officially in charge of creating and enforcing all security policies.
- Workforce Security: Clear procedures must exist for authorizing, supervising, and terminating employee access to PHI.
- Information Access Management: Strict policies must be in place to ensure employees only access the absolute minimum PHI needed to do their jobs.
- Security Awareness and Training: Every single person who comes into contact with PHI needs regular, ongoing training on security protocols.
To keep up with these rules, especially risk analysis, many organizations use effective HIPAA risk assessment tools. Ultimately, these safeguards make sure every team member knows their role in keeping patient data safe.
Physical Safeguards: The Secure Vault
Next, we have Physical Safeguards. This pillar is all about protecting the actual hardware and equipment where electronic PHI (ePHI) lives. If administrative safeguards are the rules, physical safeguards are the locked doors, security cameras, and secure server racks.
These measures are designed to stop unauthorized people from physically getting their hands on sensitive data. A transcription service absolutely must prove it has control over its physical environment.
A vendor’s data security is only as strong as its weakest physical link. A state-of-the-art encryption system means nothing if the server it runs on is sitting in an unlocked, unsupervised room.
Examples of critical physical safeguards include:
- Facility Access Controls: Implementing procedures to limit who can physically enter areas where ePHI is stored, while making sure authorized staff can get in when they need to.
- Workstation Use: Policies that dictate how workstations accessing ePHI can be used, like making sure they aren't left unattended in public areas.
- Workstation Security: Putting physical locks and other protections on all workstations that handle ePHI to restrict access.
- Device and Media Controls: Documented procedures for how hardware and electronic media are moved, reused, or securely destroyed.
These controls ensure that laptops, servers, and other devices are physically safe from theft or tampering. You can usually find out how a company handles this by checking out its official documentation. For instance, you can read about our commitment in our privacy policy.
Four Pillars of Real-World HIPAA Protection
Secure Access Control
Only authorized roles gain entry to systems containing PHI. This prevents accidental exposure by staff who don’t need clinical-level data. It enforces strict access hygiene inside healthcare environments.
Physical Device Security
Servers, laptops, and storage devices must be physically protected. Locks, restricted rooms, and monitored environments ensure no unauthorized person can touch PHI hardware.
Safe Data Transfer
Any PHI moving between devices or systems must follow encrypted, monitored pathways. Secure transfer methods eliminate interception threats during uploads and downloads.
Verified Audit Trails
Every action, login, and data interaction is automatically recorded. These logs prove compliance, support investigations, and maintain a transparent record for accountability.
Technical Safeguards: The Digital Locks
Finally, there are the Technical Safeguards. This is the technology—the software and policies—used to protect ePHI and control who can access it. These are the digital locks, alarms, and surveillance systems that work on the data itself.
This is what most people immediately think of when they hear "data security," and it includes some of the most important features of any compliant platform.
Smart Features That Boost Accuracy & Clinical Efficiency

Speaker detection
Automatically identify different speakers in your recordings and label them with their names.
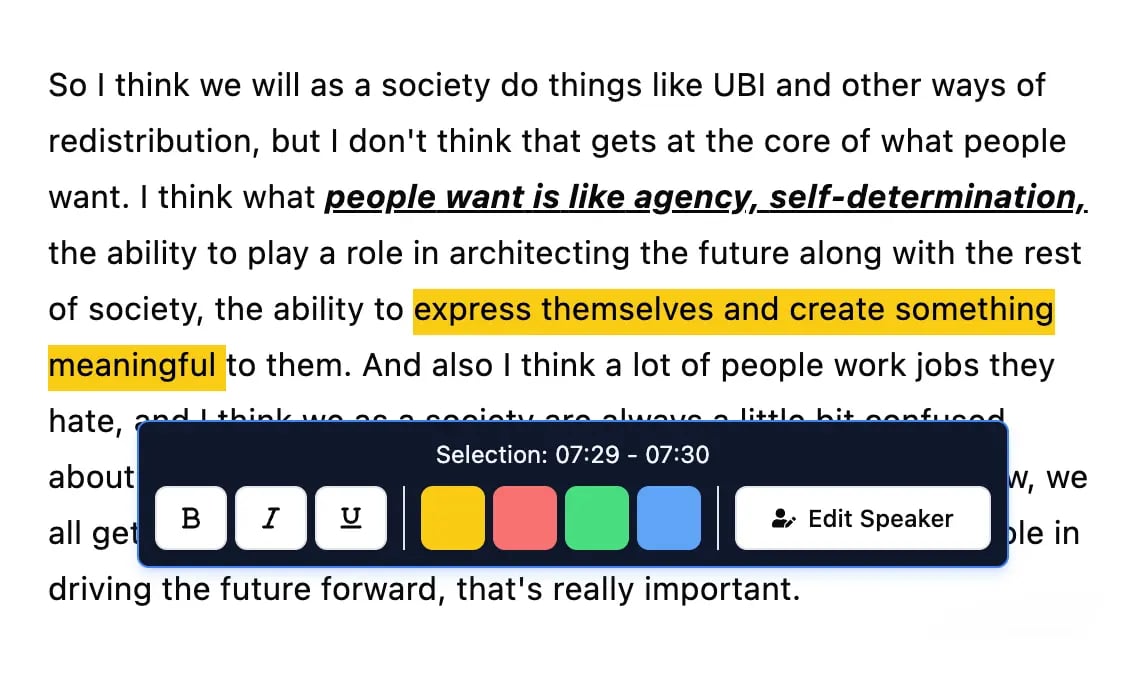
Editing tools
Edit transcripts with powerful tools including find & replace, speaker assignment, rich text formats, and highlighting.
Summaries and Chatbot
Generate summaries & other insights from your transcript, reusable custom prompts and chatbot for your content.
Key Technical Safeguards:
- Access Control: This means using technology to ensure only authorized people can access ePHI. It involves things like unique user IDs, automatic logoff timers, and encryption.
- Audit Controls: Hardware and software must be in place to record and examine all activity on systems that contain or use ePHI. You need a trail of who did what, and when.
- Integrity Controls: Policies must prevent ePHI from being improperly changed or deleted. This is often handled with tools like digital signatures that verify data hasn't been tampered with.
- Transmission Security: This safeguard demands technical measures to protect ePHI while it's being sent over a network. End-to-end encryption is the undisputed standard here.
Together, these three pillars form a complete, multi-layered defense system. A truly HIPAA compliant transcription service will have strong, documented measures covering all three, giving you peace of mind that your patient data is protected from every conceivable threat.
Why a Business Associate Agreement Is Non-Negotiable
Before you even think about sending a single audio file with Protected Health Information (PHI) to a vendor, there’s one document that acts as the gatekeeper for compliance: the Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
This isn't just another piece of paperwork to check off a list. It's a legally binding contract that is absolutely essential when you work with any third-party service, especially a transcription provider.
Think of it as the ultimate prenup for your data. A BAA clearly outlines the roles, responsibilities, and—most importantly—the liabilities of both your organization (the "Covered Entity") and the transcription service (the "Business Associate"). Without it, you’re just handing over incredibly sensitive patient data with no legal framework to protect it or hold the vendor accountable if something goes wrong.
This agreement elevates a simple vendor relationship into a genuine partnership in security. It legally forces the transcription service to play by the same strict HIPAA rules you do.
What a BAA Actually Does
A BAA is so much more than a simple promise to "keep data safe." It’s a detailed contract that spells out specific obligations, making sure the vendor is an active participant in your compliance strategy, not a passive one. Any legitimate HIPAA compliant transcription service will have a BAA ready to go and will sign it without a second thought.
A solid BAA has to lock down several key points:
- Permitted Uses of PHI: It explicitly states how the business associate can use and disclose PHI, strictly limiting it to the transcription services you’ve agreed upon. No more, no less.
- Implementation of Safeguards: The agreement requires the vendor to implement all the necessary administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect the integrity of the PHI.
- Breach Notification Protocol: It sets up a clear, immediate process for the vendor to report any data breach or security incident back to you. No delays, no excuses.
- Subcontractor Compliance: It ensures that any subcontractors the vendor uses are also bound by the same HIPAA rules, extending the chain of trust and accountability.
A vendor refusing to sign a BAA is the biggest red flag you will ever see. It’s a clear signal that they are either unwilling or unable to meet the baseline legal requirements for handling PHI, and that puts your entire organization at risk.
Never Work With a Vendor Who Won’t Sign a BAA
A valid HIPAA relationship cannot exist without a signed BAA. This contract defines responsibilities, safeguards, and accountability. If a vendor hesitates or refuses, it means they’re not equipped to protect PHI—and your organization carries all the legal risk.
The Legal and Financial Stakes
Operating without a BAA isn't just sloppy—it's a direct violation of HIPAA. If a data breach happens on your transcription vendor's end, the absence of a signed BAA means all the legal and financial fallout could land squarely on your shoulders.
A Business Associate Agreement shifts liability. It legally binds your vendor to protect patient data, making them a co-defendant in the event of a breach. Without it, you alone may be held responsible for their security failures.
The consequences can be brutal, ranging from massive fines from the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to permanent damage to your organization's reputation. Patients trust you with their most private information; that trust is shattered when a partner handles it carelessly.
For a deeper dive into what a secure provider's commitments look like, you can explore the details of a strong security posture, which is the bedrock of any trustworthy BAA.
Ultimately, the BAA is your first and most critical line of defense. It ensures any HIPAA compliant transcription services you use are not just another tool, but a fully accountable partner in protecting patient privacy.
Essential Features of a Secure Transcription Service

A signed BAA is just the entry ticket. The real security of a HIPAA compliant transcription service lies in its technology. These features aren't just nice-to-haves; they're the fundamental building blocks that keep Protected Health Information (PHI) safe from the moment you hit "upload" to the moment you get your transcript back.
Think of it like evaluating a bank vault. You wouldn't just trust the sign on the door—you'd want to know about the thickness of the walls, the type of lock, and the surveillance system. A truly compliant platform has layers of defense designed to protect data against any threat.
End-to-End Encryption as the Standard
The absolute, non-negotiable starting point is end-to-end encryption. Imagine it as a digital armored truck. From the second your audio file leaves your computer until you download the finished transcript, it’s scrambled into unreadable code.
This protection is crucial in two states:
- Data in Transit: This shields your files as they travel across the internet to the service's servers, preventing anyone from "eavesdropping" along the way.
- Data at Rest: This secures your files while they’re stored on the server. Even if someone broke in and physically stole the hard drive, the encrypted data would be completely useless without the decryption keys.
Any service that only encrypts data in one state is leaving the door wide open. True HIPAA compliance means PHI is protected around the clock, no exceptions.
Granular Access Controls and User Authentication
Not everyone in your practice needs to see every patient record. That's what granular access controls are for. This lets an administrator decide exactly who can see and do what, ensuring people only have access to the information required for their job.
It’s all about the "principle of least privilege." A billing specialist might need to see transcripts related to an insurance claim, but they shouldn't have access to unrelated clinical psychology notes.
A secure system doesn't just keep unauthorized people out; it carefully manages what authorized people can do inside. This is the difference between a simple lock and a full security detail.
On top of that, strong user authentication—like requiring complex passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA)—adds another critical layer. It proves that the person logging in is who they say they are, stopping bad actors who might have stolen a password.
Comprehensive Audit Logs for Accountability
If something goes wrong, how would you trace the steps? Comprehensive audit logs are the answer. These are detailed, unchangeable records of every single action taken inside the system.
A proper audit trail tracks everything that matters:
- Who accessed the data (the specific user account).
- What data they accessed (which transcript or file).
- When they accessed it (a precise timestamp).
- What they did (viewed, edited, deleted, or downloaded).
These logs are indispensable for accountability and for investigating any potential breach. They create a transparent record that proves a service is serious about monitoring and managing data access. Many HIPAA-compliant transcription services use advanced medical transcription software with these logging capabilities built right in.
Secure Data Management and Deletion Policies
Finally, a compliant service needs a clear plan for data from creation to destruction. This includes defining how long data is stored and having a bulletproof process for permanently deleting it when it's no longer needed. A "zero-storage" policy, where recordings are automatically scrubbed after transcription, is a great sign of a security-first approach.
These advanced technologies are quickly becoming the industry norm. By 2025, it's expected that over 60% of healthcare providers will use cloud-based transcription platforms that adhere to both HIPAA and GDPR. These platforms rely on strong encryption and MFA to lock down patient information and minimize breach risks.
Together, these features create the technological backbone of a service you can trust. As you weigh your options, it's helpful to see how modern tools work, especially when looking at AI-powered transcription software that can deliver both speed and security when built the right way.
Choosing the Right Compliant Transcription Partner
Picking a transcription service isn't just another vendor choice. It's a critical decision that directly impacts your organization's security and legal standing. The right partner is more than a tool; they're an extension of your commitment to patient privacy, armed with the tech and policies to prove it.
This is why the first thing we do at Transcript.LOL is offer to sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with any covered entity. This isn't up for debate—it's our foundational promise. By signing a BAA, we legally bind ourselves to the same strict HIPAA standards you follow. We're an accountable partner in protecting PHI, period.
The Technology Behind Trust
A BAA provides the legal framework, but it's the technology that actually does the protecting. A trustworthy partner needs a modern infrastructure built to defend against today’s threats. Our platform uses end-to-end encryption, which means your data is secure both while it's being uploaded (in transit) and while it's stored on our servers (at rest).
Think of it like this: your data gets loaded into a digital armored truck the moment it leaves your system and stays locked in a secure vault until you need it again. This layered approach ensures that even if someone physically breached our servers—a highly unlikely event—the information would be unreadable and totally useless. That's the level of security that defines a modern, HIPAA-compliant transcription service.
The Critical Importance of a No-Training Policy
In the age of AI transcription, there’s one question that trumps all others: what happens to your data after the transcript is finished? A lot of AI services use customer data to train their models. When you're dealing with PHI, that's completely unacceptable. This is where a strict no-training policy makes all the difference.
At Transcript.LOL, we guarantee that your sensitive audio and video files are never, under any circumstances, used to train our AI models. Your data is processed for one reason only: to generate your transcript. After that, it's handled according to our secure data protocols.
An AI service using your PHI for model training is like a bank using your private financial records to train its tellers. It’s a fundamental breach of privacy, and our no-training policy ensures this line is never crossed.
This commitment creates a hard boundary, guaranteeing complete data privacy and isolation. It means the details of a patient consultation, a therapy session, or a medical review will never become part of some massive dataset. It’s an essential pillar for maintaining patient confidentiality and trust.
Ultimately, choosing the right partner comes down to these core commitments: a readily available BAA, powerful encryption, and an explicit no-training data policy. For any healthcare organization, these elements are non-negotiable. They are the pillars that make Transcript.LOL a secure, efficient, and reliable choice for modern healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions About HIPAA Transcription
Navigating the world of HIPAA-compliant transcription can feel like a maze. But once you grasp a few core concepts, it all starts to click. Here are some clear, straightforward answers to the questions we hear most often.
Can I Use a Standard Service if I Remove Patient Names?
Unfortunately, no. Simply stripping out a patient's name isn't nearly enough to make health information anonymous under HIPAA. The regulation explicitly lists 18 specific identifiers that are considered Protected Health Information (PHI).
These identifiers go way beyond just names. They include things like medical record numbers, dates related to care, and even specific geographic details. If any of these are present, the data can potentially be traced back to an individual. Using a non-compliant service for audio with any PHI—even if you think you’ve scrubbed it—is a serious violation that opens your practice up to huge legal risks. The only safe way forward is to use a fully compliant service and have a signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA) in place.
Think of it this way: redacting a name is like blurring a single face in a group photo where everyone is wearing a uniform with a name tag. True de-identification is far more involved, and HIPAA demands a service built to handle all 18 identifiers with airtight security.
What Happens if My Transcription Provider Has a Data Breach?
If your transcription partner has a data breach, the BAA they signed with you legally requires them to notify you without "unreasonable delay." That agreement should spell out exactly who is responsible for what, creating a clear game plan for responding to the incident.
But here’s the critical part: as the Covered Entity, the ultimate responsibility still rests with you. You're the one on the hook for notifying affected patients and the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) about the breach. This is precisely why it’s so important to scrutinize a vendor’s security and their breach notification plan before you sign anything.
Is AI-Powered Transcription Safe for Medical Records?
Yes, AI transcription can be incredibly secure and 100% HIPAA compliant—but only if the platform was designed from the ground up with security as its core focus. A compliant AI service isn't just about accurate text; it's about the deep-seated security measures protecting that text.
Any AI platform you consider must have:
- End-to-End Encryption: Data has to be locked down both in transit (as it's uploaded) and at rest (while it's stored).
- Strict Access Controls: Only authorized users should ever be able to see or touch sensitive information.
- Comprehensive Audit Trails: You need a complete log of every single interaction with the data. No exceptions.
The single most important factor, though, is the provider's data usage policy. A truly secure service like Transcript.LOL operates on a strict "no-training" policy. This is your guarantee that sensitive patient data is never, ever used to train AI models. It’s processed only for your transcription and then it’s hands-off, ensuring total privacy.
Start Your HIPAA-Compliant Transcription in Minutes
Our platform keeps PHI fully secure, never trains AI models on your data, and includes every required safeguard. Begin using fast, accurate, encrypted transcription with full HIPAA compliance today.
Ready to see how a truly secure, AI-powered transcription service can transform your workflow? Get started with Transcript.LOL and experience fast, accurate, and confidential transcription you can trust. Learn more and sign up today.
