Von Ton zu Text Ihr Leitfaden zu Speech-to-Text-Software
Entdecken Sie, wie Speech-to-Text-Software Audio in wertvolle Inhalte umwandelt. Erfahren Sie, wie es funktioniert, welche Funktionen wichtig sind und wie Sie das richtige Tool auswählen.
Praveen
February 17, 2025
Speech-to-Text-Software ist die Magie, die gesprochene Wörter aus einer Audiodatei in einfachen, nutzbaren Text umwandelt. Stellen Sie es sich wie Ihren eigenen digitalen Stenografen vor, der bereit ist, Aufnahmen, Besprechungen oder Sprachnotizen anzuhören und in wenigen Minuten ein bearbeitbares, durchsuchbares Dokument zu erstellen. Es ist ein Muss für jeden, der viel Zeit sparen und seine Audioinhalte viel nützlicher machen möchte.
Entschlüsseln Sie Ihr Audio: Von Schallwellen zu durchsuchbarem Text
KI-Transkriptionsfunktionen
Modernste KI
Angetrieben von OpenAIs Whisper für branchenführende Genauigkeit. Unterstützung für benutzerdefinierte Vokabulare, bis zu 10 Stunden lange Dateien und ultraschnelle Ergebnisse.

Aus mehreren Quellen importieren
Importiere Audio- und Videodateien aus verschiedenen Quellen, einschließlich direktem Upload, Google Drive, Dropbox, URLs, Zoom und mehr.

Sprechererkennung
Identifiziere automatisch verschiedene Sprecher in deinen Aufnahmen und beschrifte sie mit ihren Namen.
Stellen Sie sich Folgendes vor: Sie haben gerade eine brillante zweistündige Podcast-Episode oder eine Reihe von tiefgehenden Kundeninterviews abgeschlossen. Diese Audioaufnahmen sind voller Gold – wertvolle Erkenntnisse, zündende Zitate und bahnbrechende Ideen – aber sie stecken alle in einer Audiodatei fest. Sie können sie nicht durchsuchen, nicht einfach zitieren, und die Wiederverwendung ist ein Albtraum. Sie sitzen vor einem Berg von Audio mit der zermürbenden Aufgabe, jedes einzelne Wort abzutippen.
Dies ist ein klassischer Engpass für Kreative, Forscher, Vermarkter und Studenten gleichermaßen. All die Zeit, die man über einer Tastatur verbringt und manuell transkribiert, könnte für Analysen, die Erstellung neuer Inhalte oder tatsächliches strategisches Denken verwendet werden. Spracherkennungssoftware durchbricht diese Barriere und fungiert als Brücke zwischen Ihren gesprochenen Worten und umsetzbaren, digitalen Inhalten.
Aber diese Technologie tippt nicht mehr nur für Sie; sie erschließt das verborgene Potenzial in Ihrem Audio. Sie verwandelt Ihre Audio- und Videodateien von statischen Aufnahmen in dynamische, vielseitige Assets.
- Auffindbarkeit: Eine Transkription macht Ihre Audioinhalte für Suchmaschinen indizierbar und hilft einem ganz neuen Publikum, Ihre Arbeit zu finden.
- Zugänglichkeit: Sie bietet eine Textalternative für Menschen, die gehörlos oder schwerhörig sind, und erweitert sofort Ihre Reichweite.
- Wiederverwendung: Sie ermöglicht es Ihnen, schnell Zitate für soziale Medien zu extrahieren, Interviews in Blogbeiträge umzuwandeln oder detaillierte Shownotes zu erstellen, ohne ins Schwitzen zu geraten.
Die Nachfrage danach explodiert. Der globale Markt für Spracherkennungs-APIs wurde 2021 auf 2,2 Milliarden US-Dollar bewertet und wird voraussichtlich bis 2026 5,4 Milliarden US-Dollar erreichen. Dieses unglaubliche Wachstum zeigt nur, wie unverzichtbar Sprachtechnologie in fast jeder Branche geworden ist. Die vollständige Aufschlüsselung finden Sie in diesem detaillierten Bericht über den Markt für Spracherkennungs-APIs.
Im Wesentlichen ist der Prozess ziemlich einfach. Wenn Sie die grundlegenden Mechanismen verstehen möchten, können Sie erfahren, wie Sie eine Transkription aus jeder Audiodatei erstellen. Moderne Tools haben dies extrem vereinfacht und liefern Ihnen mit fast keinem Aufwand ein hochpräzises Dokument. Das Hinzufügen von Funktionen wie Zeitstempeln ist ebenfalls ein entscheidender Vorteil für die Synchronisierung von Text mit Audio, was für Videoeditoren und Forscher eine enorme Hilfe ist. Um zu sehen, wie das funktioniert, lesen Sie unseren Leitfaden zur Transkription mit Timecode für punktgenaue Genauigkeit.
Wie KI lernt zuzuhören und zu transkribieren
Haben Sie schon einmal Spracherkennungssoftware verwendet? Es kann sich wie Magie anfühlen. Sie laden eine Audiodatei hoch oder beginnen zu sprechen, und Momente später erscheint eine nahezu perfekte Transkription auf Ihrem Bildschirm. Aber hinter diesem scheinbar einfachen Prozess verbirgt sich eine faszinierende Zusammenarbeit verschiedener KI-Modelle, die zusammenarbeiten, um zuzuhören, zu verstehen und zu schreiben – ganz ähnlich wie ein Mensch.
Stellen Sie sich das wie das Training eines brandneuen Stenografen vor. Zuerst muss er lernen, einzelne Laute zu unterscheiden. Dann muss er diese Laute als Wörter erkennen. Schließlich muss er diese Wörter zu Sätzen zusammenfügen, die tatsächlich Sinn ergeben. Eine KI folgt einem überraschend ähnlichen Weg, um ihre hohe Genauigkeit zu erreichen.
Der gesamte Prozess beginnt, sobald die Software Ihre Audiodatei erhält. Sie beginnt damit, die kontinuierliche Schallwelle Ihrer Stimme in Tausende winziger, einzelner Toneinheiten zu zerlegen. Diese werden Phoneme genannt – die kleinsten Bausteine der gesprochenen Sprache, wie das "k" in "Katze" oder das "sch" in "Schuh".
Das akustische Modell: Wörter hören
Sobald das Audio in diese grundlegenden Toneinheiten zerlegt ist, tritt das akustische Modell in Aktion. Das ist das Ohr der KI. Es wurde anhand einer riesigen Bibliothek gesprochener Sprache trainiert, die Hunderttausende von Stunden Audio enthält, die sorgfältig mit ihren Texttranskriptionen abgeglichen wurden.
Dieses intensive Training macht das akustische Modell zu einem Experten für eine Sache: das Abgleichen der eingehenden Phoneme mit den Buchstaben und Wörtern, die es bereits kennt. Es analysiert die spezifischen Frequenzen und Muster jedes Klangs und trifft eine fundierte Vermutung, indem es fragt: "Passt dieser kleine Klangschnipsel zum Phonem für 't', 'o' oder 'p'?"
Natürlich ist dies allein selten perfekt. Dinge wie Akzente, Hintergrundgeräusche oder einfach nur schnelles Sprechen können das akustische Modell leicht aus dem Tritt bringen. Das Ergebnis kann ein Durcheinander von Wörtern sein, die richtig klingen, aber absolut keinen Sinn ergeben. Hier kommt die nächste KI-Schicht ins Spiel.
Dieses Diagramm zeigt den grundlegenden Ablauf von einer Schallwelle zu einem fertigen Textdokument.
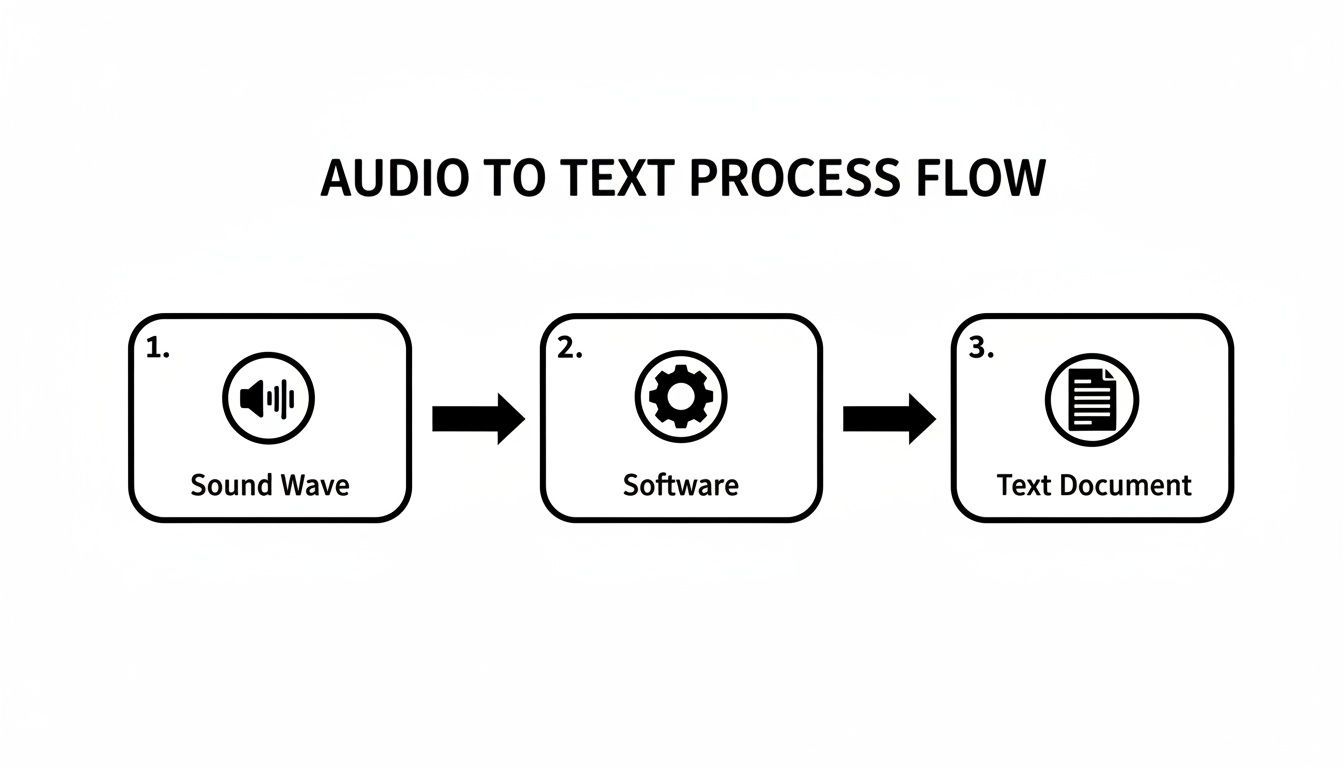
Diese einfache Umwandlung wird durch komplexe KI-Modelle angetrieben, die zusammenarbeiten, um sicherzustellen, dass der endgültige Text sowohl genau als auch lesbar ist.
Das Sprachmodell: Sinn ergeben
Nachdem das akustische Modell seinen Rohentwurf ausgespuckt hat, übernimmt das Sprachmodell. Sie können sich das als das Gehirn der KI oder ihren internen Redakteur vorstellen. Während es beim akustischen Modell um Laute geht, dreht sich beim Sprachmodell alles um Kontext, Grammatik und Wahrscheinlichkeit.
Es wurde anhand einer gigantischen Textbibliothek trainiert – Bücher, Artikel, Websites, was auch immer – und hat daher ein tiefes Verständnis dafür, wie Wörter zusammenpassen sollten. Es betrachtet die holprige Ausgabe des akustischen Modells und beginnt, kritische Fragen zu stellen:
- Grammatik: Ist dieser Satz korrekt aufgebaut?
- Kontext: Folgt dieses Wort logisch auf das vorherige?
- Wahrscheinlichkeit: Ist es wahrscheinlicher, dass der Sprecher "Ich schreie nach Eis" oder "Augen schreien nach Augen" gesagt hat?
Ein akustisches Modell könnte zum Beispiel "recognize speech" und "wreck a nice beach" als nahezu identisch hören. Aber das Sprachmodell weiß, dass "recognize speech" ein viel gebräuchlicherer und logischerer Ausdruck ist, insbesondere im Kontext einer Transkription. Es korrigiert solche Fehler, glättet umständliche Formulierungen und fügt sogar Satzzeichen basierend auf den Pausen und der Intonation des Sprechers hinzu. Dieses zweiteilige System ist das Geheimnis, wie Audio-zu-Text-KI so beeindruckende Ergebnisse erzielt.
Warum zwei Modelle wichtig sind
Akustische Modelle konzentrieren sich auf die Genauigkeit des Tons, während Sprachmodelle für Kontext und Lesbarkeit sorgen. Zusammen reduzieren sie Fehler, die durch Akzente, Homophone und unklare Aussprache verursacht werden. Dieser mehrschichtige Ansatz ist der Grund, warum moderne Speech-to-Text-Tools ältere Diktatsysteme übertreffen.
Wichtigste Erkenntnis: Die Genauigkeit von Speech-to-Text-Software beruht auf einem leistungsstarken Duo. Das akustische Modell wandelt rohe Geräusche in eine Liste wahrscheinlicher Wörter um, und das Sprachmodell nutzt Kontext und Grammatik, um diese Liste in kohärenten, genauen Text zu verwandeln.
Diese gesamte Zusammenarbeit geschieht in Sekundenbruchteilen und verwandelt einen unordentlichen Audiostream in ein sauberes, strukturiertes Dokument, das Sie sofort verwenden können.
Ihr Werkzeugkasten: Wesentliche und erweiterte Funktionen
Die Wahl der richtigen Speech-to-Text-Software ist ein bisschen wie die Wahl eines Autos. Eine einfache Limousine bringt Sie problemlos von A nach B. Aber wenn Sie schwere Ausrüstung transportieren müssen, benötigen Sie einen speziellen LKW.
Auf die gleiche Weise kann fast jedes Werkzeug Audio in Wörter umwandeln, aber die besten sind mit Funktionen ausgestattet, die anspruchsvolle, spezifische Arbeitsabläufe bewältigen, ohne ins Schwitzen zu geraten. Um das Richtige auszuwählen, müssen Sie die unverzichtbaren von den wünschenswerten Funktionen trennen.
Die Nichtverhandelbaren: Kernfunktionen für die Transkription
Bevor Sie sich von glänzenden Extras ablenken lassen, müssen Sie sicherstellen, dass die Software die Grundlagen beherrscht. Dies sind die Säulen, die ein Werkzeug wirklich nützlich und nicht zu einer ständigen Frustrationsquelle machen.
Betrachten Sie diese als den Motor, die Räder und das Lenkrad Ihres Transkriptionsfahrzeugs – wenn Sie diese falsch machen, kommen Sie nirgendwohin.
- Hohe Genauigkeit: Das ist alles. Ein fehlerhaftes Transkript verursacht mehr Arbeit, als es spart, und Sie verbringen Stunden mit Korrekturen. Sie sollten nach Plattformen suchen, die bei klarem Audio durchweg eine Genauigkeit von 95 % oder höher erreichen.
- Breite Unterstützung für Dateiformate: Ihre Audio- und Videodateien gibt es in allen Formen und Größen. Ein gutes Werkzeug sollte gängige Formate wie MP3, MP4, M4A und WAV verarbeiten können, ohne dass Sie Dateien zuerst konvertieren müssen.
- Großzügige Dateigrößenbeschränkungen: Projekte in der realen Welt bedeuten oft Langform-Inhalte. Ob es sich um einen zweistündigen Podcast oder eine ganztägige Konferenz handelt, die Software muss große Dateien und lange Aufnahmen verarbeiten können, ohne ins Stocken zu geraten.
Diese drei Funktionen sind die absolute Basis für jede effektive Speech-to-Text-Software. Sie machen ein Werkzeug zuverlässig und flexibel genug für die tatsächliche Arbeit.
Über die Grundlagen hinaus: Erweiterte Funktionen, die ernsthaft Zeit sparen
Sobald ein Werkzeug die Grundlagen beherrscht, ist es an der Zeit, sich die erweiterten Funktionen anzusehen. Hier wird ein guter Dienst zu einem großartigen, der ein einfaches Transkriptionstool in ein echtes Produktivitätskraftpaket verwandelt.
Produktivitäts- und Exportfunktionen
Bearbeitungswerkzeuge
Bearbeite Transkripte mit leistungsstarken Werkzeugen wie Suchen und Ersetzen, Sprecherzuordnung, Rich-Text-Formate und Hervorhebungen.
In mehreren Formaten exportieren
Exportiere deine Transkripte in mehreren Formaten, einschließlich TXT, DOCX, PDF, SRT und VTT mit anpassbaren Formatierungsoptionen.
Zusammenfassungen und Chatbot
Erstelle Zusammenfassungen und andere Erkenntnisse aus deinem Transkript, wiederverwendbare benutzerdefinierte Prompts und Chatbot für deine Inhalte.
Dies sind die GPS, der Allradantrieb und der zusätzliche Laderaum Ihrer Software – sie helfen Ihnen, knifflige Projekte zu meistern, eine höhere Arbeitslast zu bewältigen und unter schwierigen Bedingungen Leistung zu bringen. Und der Markt für diese Tools explodiert. Der Markt für Speech-to-Text-APIs wurde im Jahr 2023 auf 2,77 Milliarden US-Dollar bewertet und wird voraussichtlich bis 2032 9,86 Milliarden US-Dollar erreichen, so ein aktueller Bericht über den Markt für Speech-to-Text-APIs.
Wichtige Erkenntnis: Für Fachleute sind erweiterte Funktionen nicht nur Vorteile. Sie führen direkt zu Zeitersparnis, höherer Arbeitsqualität und reibungsloseren Arbeitsabläufen.
Hier sind die entscheidenden Funktionen, auf die Sie achten sollten:
- Automatische Sprechererkennung (Diarisierung): Dies ist ein Lebensretter für jede Aufnahme mit mehreren Personen – Interviews, Besprechungen, Fokusgruppen, was auch immer. Die Software erkennt automatisch, wer spricht, und kennzeichnet den Dialog ("Sprecher 1", "Sprecher 2"), was Ihnen die mühsame manuelle Arbeit erspart.
- Benutzerdefiniertes Vokabular: Standard-KI-Modelle stolpern oft über Branchenjargon, Unternehmenskürzel oder einzigartige Namen. Eine Funktion für benutzerdefinierte Vokabulare ermöglicht es Ihnen, der KI diese spezifischen Begriffe "beizubringen", was die Genauigkeit für spezialisierte Inhalte in Bereichen wie Medizin, Recht oder Technologie erheblich verbessert.
- Nahtlose Integrationen: Die besten Tools funktionieren gut mit anderen zusammen. Achten Sie auf Integrationen mit Plattformen, die Sie bereits nutzen, wie z. B. Google Drive, Dropbox oder YouTube. Dies schafft einen automatisierten Workflow, bei dem Ihre Dateien automatisch transkribiert werden, ohne dass manuelle Uploads erforderlich sind. Unser Leitfaden zu KI-gestützter Transkriptionssoftware zeigt, wie diese Verbindungen ein wesentlich effizienteres System schaffen.
- Vielseitige Exportoptionen: Eine einfache .txt-Datei reicht oft nicht aus. Erstklassige Plattformen ermöglichen den Export von Transkripten in mehreren Formaten, wie z. B. DOCX für Berichte, SRT/VTT für Videountertitel und PDFs für die einfache Weitergabe. Diese Flexibilität macht Ihr Transkript sofort für jeden Bedarf nutzbar.
- Robuste Datenschutzrichtlinie: Dies ist ein wichtiger Punkt. Wenn Sie sensible Gespräche hochladen, müssen Sie sicher sein, dass Ihre Daten sicher sind. Wählen Sie nur einen Anbieter mit einer klaren Datenschutzrichtlinie, die garantiert, dass Ihre Daten nicht zum Trainieren ihrer KI-Modelle verwendet werden. Dies ist der einzige Weg, um sicherzustellen, dass Ihre vertraulichen Informationen vertraulich bleiben.
Um Ihnen bei der Entscheidung zu helfen, was für Sie richtig ist, hier eine kurze Aufschlüsselung der wesentlichen Funktionen im Vergleich zu den erweiterten Funktionen.
Wesentliche vs. Erweiterte Speech-to-Text-Funktionen
| Funktion | Was es tut | Wer braucht es am meisten |
|---|---|---|
| Hohe Genauigkeit | Liefert ein Transkript mit minimalen Fehlern, das wenig bis gar keine Korrektur erfordert. | Jeder. Dies ist die grundlegende Anforderung für jedes nützliche Transkriptionstool. |
| Breite Unterstützung von Dateiformaten | Akzeptiert gängige Audio- und Videodateien (MP3, MP4, WAV) ohne Konvertierung. | Benutzer, die mit verschiedenen Medienquellen arbeiten und sich nicht mit der Dateivorbereitung herumschlagen wollen. |
| Großzügige Dateilimitierungen | Verarbeitet lange Aufnahmen (z. B. 2+ Stunden) und große Dateigrößen ohne Fehler. | Podcaster, Forscher, Journalisten und alle, die sich mit Langform-Inhalten beschäftigen. |
| Sprechererkennung | Identifiziert und kennzeichnet automatisch verschiedene Sprecher im Transkript (z. B. "Sprecher 1"). | Interviewer, Besprechungsorganisatoren und qualitative Forscher, die zwischen Stimmen unterscheiden müssen. |
| Benutzerdefiniertes Vokabular | Ermöglicht das Hinzufügen spezifischer Begriffe, Namen oder Fachjargon zur Verbesserung der Erkennungsgenauigkeit. | Fachleute in technischen Bereichen (Medizin, Recht, Finanzen), wo Präzision entscheidend ist. |
| Integrationen | Verbindet sich mit anderen Apps wie Google Drive oder YouTube, um den Transkriptionsworkflow zu automatisieren. | Content-Ersteller, Vermarkter und Teams, die effiziente, automatisierte Content-Pipelines aufbauen möchten. |
| Vielseitige Exportoptionen | Ermöglicht den Download von Transkripten in mehreren Formaten (DOCX, SRT, VTT, PDF) für verschiedene Zwecke. | Videoeditoren, die Untertitel benötigen, Autoren, die Berichte entwerfen, und alle, die Inhalte auf mehreren Plattformen wiederverwenden. |
| Datenschutzgarantien | Stellt sicher, dass Ihre vertraulichen Audio-/Videodateien nicht zum Trainieren von KI-Modellen verwendet werden. | Juristen, Therapeuten, Unternehmensteams und alle, die sensible oder proprietäre Informationen verarbeiten. |
Letztendlich ist das beste Tool eines, das in Ihren Workflow passt. Indem Sie den Unterschied zwischen den Kernnotwendigkeiten und den leistungsstarken Zusatzfunktionen verstehen, können Sie eine Lösung finden, die nicht nur die heutigen Probleme löst, sondern auch mit Ihnen wächst.
Transkription branchenübergreifend einsetzen
Sicher, die Technologie hinter Speech-to-Text ist faszinierend, aber sie glänzt wirklich bei der Lösung alltäglicher Probleme. Es geht nicht nur darum, Audio in Worte umzuwandeln; es ist eine Produktivitätsmaschine, die unzählige Stunden spart, neue Inhalte erschließt und Informationen in Dutzenden von Bereichen zugänglicher macht. Die Auswirkungen sind real – sie verwandeln Stunden mühsamer manueller Arbeit in Minuten fokussierter, strategischer Aktion.
Von Marketingteams bis hin zu Universitätsvorlesungssälen sind die Anwendungen ebenso vielfältig wie wertvoll. Jede Branche nutzt Transkription, um ihre eigenen einzigartigen Herausforderungen zu bewältigen, sei es die Skalierung der Content-Produktion, die Verbesserung der Studienergebnisse oder die Führung sorgfältiger Aufzeichnungen für die Einhaltung gesetzlicher und medizinischer Vorschriften.
Wie verschiedene Teams Speech-to-Text nutzen?
Content Creators
Podcaster und YouTuber verwandeln Episoden in Blogs, Untertitel und Social-Media-Posts ohne zusätzliche Aufnahmezeit. Eine Datei wird zu mehreren Content-Assets.
Forscher & Akademiker
Interviewtranskripte werden zu durchsuchbaren Datensätzen, was die qualitative Analyse beschleunigt und die Forschungsdurchlaufzeit verkürzt.
Unternehmens-Teams
Besprechungsaufzeichnungen werden in klare Protokolle, Aktionspunkte und Wissensarchive umgewandelt, die Teams auf dem Laufenden halten.
Gesundheitsfachkräfte
Ärzte diktieren Notizen direkt in Systeme, wodurch der Verwaltungsaufwand reduziert und gleichzeitig genaue medizinische Aufzeichnungen geführt werden.
Der rote Faden ist immer Effizienz. Es geht darum, Fachleute von manuellen Transkriptionsarbeiten zu entlasten, damit sie sich auf hochwertige Aufgaben konzentrieren können.
Content-Marketing und Medienproduktion
Für jeden im Marketing oder in den Medien ist eine einzelne Audio- oder Videodatei eine Goldgrube. Ein einstündiger Podcast oder ein Webinar wird nach der Transkription zum Rohmaterial für ein Dutzend anderer Inhalte. Diese "einmal erstellen, vielfach verbreiten"-Strategie ist das Geheimnis, um Ihren ROI zu maximieren und ein viel breiteres Publikum zu erreichen.
Denken Sie an ein einzelnes Podcast-Interview. Das Audio ist großartig, aber das Transkript ist ein Marketing-Schweizer Taschenmesser.
- Blogbeiträge und Artikel: Das vollständige Transkript kann zu einem umfassenden Blogbeitrag ausgearbeitet werden, angereichert mit Schlüsselwörtern, um organischen Suchverkehr anzuziehen.
- Social-Media-Inhalte: Extrahieren Sie die besten Zitate und Soundbites, um auffällige Grafiken, kurze Videoclips und prägnante Social-Media-Beiträge zu erstellen.
- E-Mail-Newsletter: Eine kurze Zusammenfassung oder eine Liste der wichtigsten Erkenntnisse ergibt einen inhaltsreichen Newsletter, der Ihr Publikum fesselt.
- Lead-Magnete: Formatieren Sie das Transkript in ein herunterladbares PDF und bieten Sie es als kostenlose Ressource an, um neue Leads zu gewinnen.
Hier kommen spezialisierte Tools ins Spiel, wie z. B. Podcast-Transkriptionstools, die zur Verbesserung der Zugänglichkeit und SEO entwickelt wurden. Dieser einfache Workflow verwandelt eine Aufnahme in eine vollständige, kanalübergreifende Marketingkampagne.
Bildung und akademische Forschung
In der akademischen Welt sind Klarheit und Zugang alles. Sprach-zu-Text-Software ist ein vollständiger Game-Changer für Studenten und Lehrende gleichermaßen, da sie gesprochene Vorlesungen und Forschungsinterviews in durchsuchbare, verdauliche Texte umwandelt.
Für Studenten ist eine transkribierte Vorlesung ein erstaunliches Lernwerkzeug. Sie können sofort nach bestimmten Begriffen oder Konzepten suchen, die ein Professor erwähnt hat, ohne stundenlanges Video durchsuchen zu müssen. Dies macht die Prüfungsvorbereitung weitaus effizienter und hilft Studenten mit unterschiedlichen Lernstilen, sich mit dem Material zu verbinden.
Forscher sehen ebenfalls massive Vorteile. Die Transkription qualitativer Interviews war früher eine schmerzhaft langsame, manuelle Arbeit. Die automatische Transkription verändert diesen Workflow vollständig und ermöglicht es Forschern, in einem Bruchteil der Zeit von der Datenerfassung zur Analyse zu gelangen. Das spart unglaublich viel Zeit und Budget.
Rechtliche und unternehmerische Umgebungen
In der juristischen und unternehmerischen Welt sind Genauigkeit und Dokumentation nicht nur wünschenswert, sondern zwingend erforderlich. Jede Besprechung, jede Aussage, jedes Kundengespräch und jede Compliance-Schulung enthält kritische Informationen, die perfekt erfasst werden müssen.
Die Verlass auf manuelle Notizen ist ein Rezept für menschliche Fehler und übersehene Details. Ein automatisierter Transkriptionsdienst liefert eine wortgetreue Aufzeichnung und schafft eine einzige, zuverlässige Wahrheitsquelle.
- Rechtliches: Anwälte können Aussagen und Gerichtsverfahren schnell durchsuchen und nach spezifischen Zeugenaussagen suchen, ohne ganze Aufnahmen erneut anhören zu müssen.
- Unternehmen: Teams können perfekte Besprechungsprotokolle erstellen, einschließlich dessen, wer was gesagt hat, um sicherzustellen, dass alle über Aktionspunkte und Entscheidungen im Bilde sind. Dies schafft Verantwortlichkeit und ein durchsuchbares Archiv des Unternehmenswissens.
Die wachsende Rolle im Gesundheitswesen
Nirgendwo ist die Notwendigkeit einer genauen, sicheren Dokumentation kritischer als im Gesundheitswesen. Die Gesundheitsbranche ist heute der am schnellsten wachsende Nutzer von Spracherkennung, angetrieben durch den Aufstieg von Fernüberwachung von Patienten, virtuellen Konsultationen und dem ständigen Bedarf an medizinischer Dokumentation.
Kliniker nutzen Sprach-zu-Text-Software, um Patientennotizen, Gesprächs-zusammenfassungen und medizinische Berichte direkt in elektronische Gesundheitsaktensysteme (EHR) zu diktieren. Dies beschleunigt nicht nur die Bürokratie, sondern reduziert auch die administrative Belastung für Ärzte und gibt ihnen mehr Zeit, sich tatsächlich um die Patienten zu kümmern.
Angesichts der Sensibilität dieser Daten sind Funktionen wie solide Datenschutzmaßnahmen und benutzerdefinierte Vokabulare für medizinische Fachbegriffe nicht verhandelbar. Um zu sehen, wie dies in der Praxis funktioniert, lesen Sie unseren Leitfaden zu medizinischen und gesundheitlichen Transkriptionsworkflows.
Optimieren Sie Ihren Workflow von Audio zu Asset
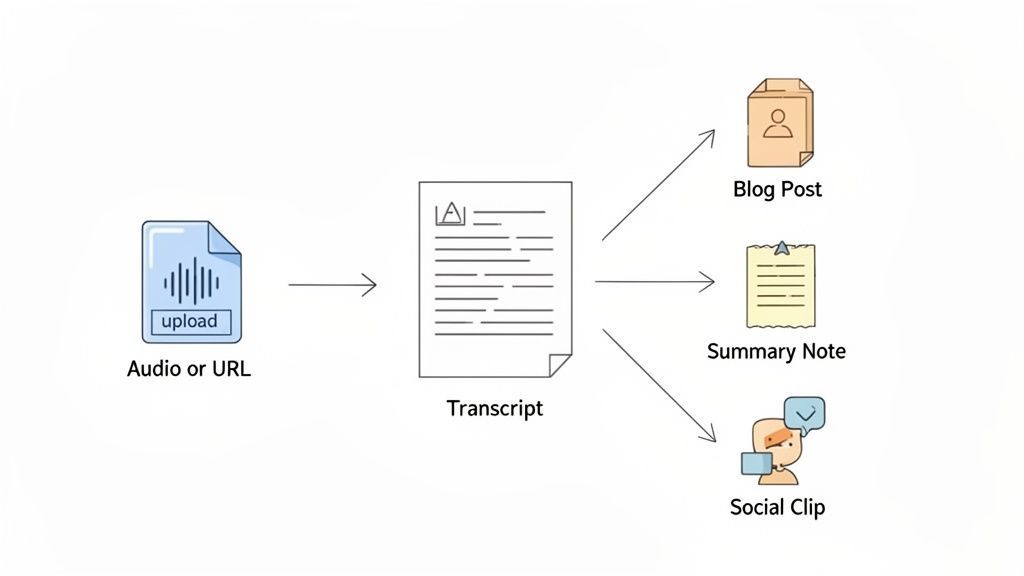
Es ist eine Sache, die Funktionen von Sprach-zu-Text-Software zu verstehen, aber eine andere, zu sehen, wie sie zu einem reibungslosen, nahtlosen Workflow zusammenpassen. Ein modernes Tool tut mehr, als nur Worte auf Papier zu bringen – es verwandelt die mühsame Transkription in eine Startrampe für alle Arten von kreativen Assets. Sie transkribieren nicht nur, Sie verwandeln eine rohe Audiodatei mit fast keiner Anstrengung in etwas Wertvolles.
Alles beginnt mit einem einfachen Schritt. Sie können eine Datei von Ihrem Computer per Drag & Drop hochladen oder Cloud-Dienste wie Google Drive und Dropbox verbinden. Viele Plattformen, einschließlich Transcript.LOL, lassen Sie sogar eine URL von YouTube oder Vimeo einfügen, und sie holen das Audio für Sie ab. Diese Flexibilität beseitigt jegliche anfängliche Hektik und zieht Ihre Inhalte sofort in das System.
In nur wenigen Minuten erledigt die KI ihre Arbeit und liefert ein hochpräzises Transkript zurück. Hier sehen Sie sofort den Wert. Anstelle eines riesigen, einschüchternden Textblocks erhalten Sie ein sauberes, strukturiertes Dokument mit automatischer Sprecherkennzeichnung. Kein Kopfzerbrechen mehr, um herauszufinden, wer was gesagt hat.
Von Rohtext zu poliertem Dokument
Sobald der erste Entwurf fertig ist, verschiebt sich Ihre Aufgabe von der Transkription zur Verfeinerung. Die besten Tools bieten Ihnen einen intuitiven Editor, in dem Sie den Text überprüfen können, während Sie die Audiowiedergabe hören. So können Sie leicht kleine Fehler korrigieren, die richtigen Sprechernamen zuweisen und Zeitstempel anpassen, um alles perfekt synchron zu halten.
Der eigentliche Zeitsparer ist jedoch die Funktion benutzerdefiniertes Vokabular. Bevor Sie überhaupt beginnen, können Sie der KI spezifische Fachbegriffe, Produktnamen oder ungewöhnliche Schreibweisen beibringen, die für Ihre Welt einzigartig sind. Wenn Sie diesen einen Schritt im Voraus machen, müssen Sie Begriffe wie "kardiopulmonal" oder einen Markennamen wie "AcuTech" nicht immer wieder manuell korrigieren.
Diese gesamte erste Phase ist auf Geschwindigkeit ausgelegt. Sie ist darauf ausgelegt, Sie in einem Bruchteil der Zeit, die es manuell dauern würde, von einer rohen Aufnahme zu einem polierten, genauen Dokument zu bringen. Das Ziel ist einfach: weniger Zeit mit Korrekturen und mehr Zeit mit der Erstellung verbringen.
Die Macht von KI-Tools nach der Transkription
Ein großartiges Transkript zu erhalten, ist nur der Anfang. Die wahre Magie moderner Plattformen liegt darin, was Sie tun können, nachdem die Worte auf der Seite stehen. Anstatt nur eine DOCX- oder SRT-Datei zu exportieren und es dabei zu belassen, können Sie integrierte KI-Tools verwenden, um Ihre Inhalte sofort wiederzuverwenden.
Stellen Sie sich vor, Sie klicken auf eine einzige Schaltfläche und erhalten:
- Eine prägnante Zusammenfassung, die eine einstündige Besprechung auf ihre wichtigsten Erkenntnisse reduziert.
- Einen veröffentlichungsfertigen Blogbeitrag, der aus einem Podcast-Interview erstellt wurde.
- Eine saubere Liste von Aktionspunkten, die aus einem Team-Brainstorming extrahiert wurde.
- Eine Handvoll ansprechender Social-Media-Beiträge, komplett mit Zitaten und Hashtags.
Das ist der große Wandel. Die Software hört auf, ein einfacher Transkriptor zu sein, und wird zu einer vollwertigen Content-Engine, die den Wert jeder einzelnen Aufnahme, die Sie machen, vervielfacht.
Natürlich muss dieser gesamte Prozess auf einer Grundlage solider Sicherheit und Privatsphäre aufgebaut sein. Wenn Sie mit sensiblen Kundengesprächen oder vertraulichen Interviews zu tun haben, müssen Sie einen Dienst nutzen, der sich zu einer strengen "No-Training"-Richtlinie verpflichtet. Dies garantiert, dass Ihre privaten Gespräche nicht zum Trainieren von KI-Modellen anderer Unternehmen verwendet werden. Ihre Daten bleiben bei Ihnen, Punkt.
Einige häufig gestellte Fragen
Die Beschäftigung mit automatisierter Transkription wirft viele Fragen auf. Es ist eine leistungsstarke Technologie, aber die Details sind entscheidend, wenn Sie das richtige Werkzeug auswählen und herausfinden, wie Sie es effektiv einsetzen. Wir haben einige der häufigsten Fragen zu Sprach-zu-Text-Software zusammengestellt, um Ihnen klare, unkomplizierte Antworten zu geben.
Betrachten Sie dies als Ihren Leitfaden, um durch den Marketing-Lärm zu navigieren. Wir werden die realen Bedenken hinsichtlich Genauigkeit, Funktionen und Sicherheit ansprechen, damit Sie eine fundierte Entscheidung treffen können.
Wie genau ist das Zeug wirklich?
Moderne KI-gestützte Dienste sind unglaublich gut geworden. Unter idealen Bedingungen – denken Sie an eine klare Audioaufnahme mit einem einzelnen Sprecher und ohne Hintergrundgeräusche – können die besten Programme über 95 % Genauigkeit erreichen. Das ist eine massive Verbesserung gegenüber den klobigen Diktierwerkzeugen der Vergangenheit, alles dank KI-Modellen, die auf unglaublichen Mengen gesprochener Sprache trainiert wurden.
Aber die reale Welt ist unordentlich. Die Genauigkeit kann sinken, wenn starke Akzente, sich überschneidende Sprecher oder einfach ein schlechtes Mikrofon ins Spiel kommen. Für spezialisierte Bereiche wie Medizin oder Recht, wo Fachbegriffe allgegenwärtig sind, kann die KI ins Stocken geraten. Deshalb ist eine Funktion für benutzerdefiniertes Vokabular für Profis so entscheidend – sie ermöglicht es Ihnen, der Software einzigartige Begriffe "beizubringen", was ihre Präzision dramatisch erhöhen kann.
Kann es mehr als einen Sprecher verarbeiten?
Ja, absolut. Tatsächlich ist dies eine der wertvollsten Funktionen, die Sie in modernen Tools finden werden. Die Magie dahinter nennt sich Sprecher-Diarisierung. Das ist ein schicker Begriff für einen einfachen Prozess: Die KI hört sich das Audio an, ermittelt, wer wann spricht, und trennt die Stimmen automatisch.
Sobald sie einen neuen Sprecher erkennt, kennzeichnet sie dessen Text entsprechend (z. B. "Sprecher 1", "Sprecher 2" usw.). Dies ist eine unverzichtbare Funktion für jeden, der transkribiert:
- Interviews
- Team-Besprechungen
- Podcasts mit mehreren Gästen
- Fokusgruppen
- Rechtliche Aussagen
Ohne sie erhalten Sie nur eine riesige Textwand. Sie müssten manuell zuhören und herausfinden, wer was gesagt hat, was ein enormer Aufwand ist. Die automatische Sprecherkennzeichnung spart Stunden Arbeit und macht das Transkript sofort nutzbar.
Was ist der Unterschied zwischen einem Transkript und Untertiteln?
Das ist eine häufige Verwechslung, aber die beiden dienen völlig unterschiedlichen Zwecken. Sie stammen beide aus demselben Audio, sind aber auf völlig unterschiedliche Weise formatiert und werden verwendet.
Wichtige Unterscheidung: Ein Transkript ist ein Textdokument zum Lesen und Analysieren. Untertitel sind zeitgesteuerte Textfragmente, die auf einem Bildschirm synchron mit einem Video erscheinen sollen.
Ein Transkript ist der vollständige Text einer Audio- oder Videodatei, typischerweise als einzelnes Dokument (wie eine DOCX- oder TXT-Datei) geliefert. Leute verwenden es, um nach Schlüsselwörtern zu suchen, Inhalte zu bearbeiten oder ein Gespräch in einen Blogbeitrag oder Artikel umzuwandeln.
Untertitel hingegen gibt es in speziellen Formaten wie SRT oder VTT. Diese Dateien zerlegen das Transkript in kleine, zeitcodierte Abschnitte. Jeder Abschnitt ist so programmiert, dass er genau in dem Moment auf dem Bildschirm erscheint, in dem die Worte gesprochen werden. Ihre Hauptaufgabe ist es, Videos für gehörlose oder schwerhörige Zuschauer zugänglich zu machen und auf Social Media Aufmerksamkeit zu erregen, wo die meisten Videos stummgeschaltet angesehen werden.
Sind meine Daten sicher, wenn ich sie hochlade?
Das ist ein wichtiger Punkt, und die Antwort hängt wirklich vom Anbieter ab, den Sie wählen. Wenn Sie eine Datei mit sensiblen Informationen hochladen – eine vertrauliche Besprechung, eine Patientenberatung, ein privates Interview – vertrauen Sie diesem Unternehmen viel an.
Gute Dienste verwenden starke Verschlüsselung, um Ihre Dateien während des Hochladens und während der Speicherung auf ihren Servern zu schützen. Aber das Wichtigste ist, die Datenschutzrichtlinie des Unternehmens zu prüfen, insbesondere was die Verwendung Ihrer Daten für das Training von KI-Modellen betrifft.
Viele Plattformen behalten sich das Recht vor, Ihre Audioaufnahmen und Transkripte zur Verbesserung ihrer eigenen KI zu verwenden. Wenn Sie vertrauliche Informationen verarbeiten, ist das ein großes Warnsignal. Sie müssen unbedingt einen Anbieter mit einer klaren und ausdrücklichen "No-Training"-Richtlinie finden. Dies garantiert, dass Ihre privaten Daten privat bleiben und niemals für etwas anderes als die Erstellung Ihres Transkripts verwendet werden. Stellen Sie Ihre Privatsphäre immer an erste Stelle.
Datenschutz ist nicht optional
Nicht alle Transkriptionsplattformen schützen Ihre Daten. Einige Anbieter verwenden hochgeladene Audios wieder, um ihre KI-Modelle zu trainieren. Überprüfen Sie immer eine klare No-Training-Richtlinie, bevor Sie vertrauliche oder sensible Aufnahmen hochladen.
Sind Sie bereit, Ihre Audio- und Videodateien in genauen, umsetzbaren Text mit einer Plattform umzuwandeln, die Ihre Privatsphäre respektiert? Transcript.LOL bietet eine KI-gestützte Lösung mit Sprechererkennung, benutzerdefiniertem Vokabular und einer strengen No-Training-Richtlinie, um Ihre Daten sicher zu halten. Erleben Sie den Unterschied, indem Sie noch heute https://transcript.lol besuchen.
Beginnen Sie noch heute mit intelligenterer Transkription
Verwandeln Sie Audio in genauen, sicheren und wiederverwendbaren Text mit KI-gestützter Transkription für Profis.
